Archamoebae Cavalier-Smith 1983
Anaerobic or microaerobic mostly ciliated amoebae with reduced mitochondrial organelles and endosymbiotic bacteria. Amoeboid movement with eruptive lobopodia. Free-living or endobiotic.
Anaerobic or microaerobic mostly ciliated amoebae with reduced mitochondrial organelles and endosymbiotic bacteria. Amoeboid movement with eruptive lobopodia. Free-living or endobiotic.
1. Mastigamoebidae Chatton 1925
Amoeboid with several pseudopodia; sometimes body stiff without amoeboid motion, depending on conditions; single cilium directed forward, with stiff vibrating beat; single kinetosome with cone of microtubules extending to nucleus; uninucleate, but some species multinucleate; stages without cilium occur; cysts; occurring in microaerobic to anaerobic habitats rich in dissolved nutrients. Free-living or endobiotic.
1.1. Mastigamoeba Schulze 1875
Amoeboid with a ciliated basal body located immediately adjacent to the nucleus. Swimming or gliding. Long cilium, directed forward while swimming. Life cycle may include amoeboid cells without cilium, multinucleate cells or cysts. Vegetative and sexual reproduction.
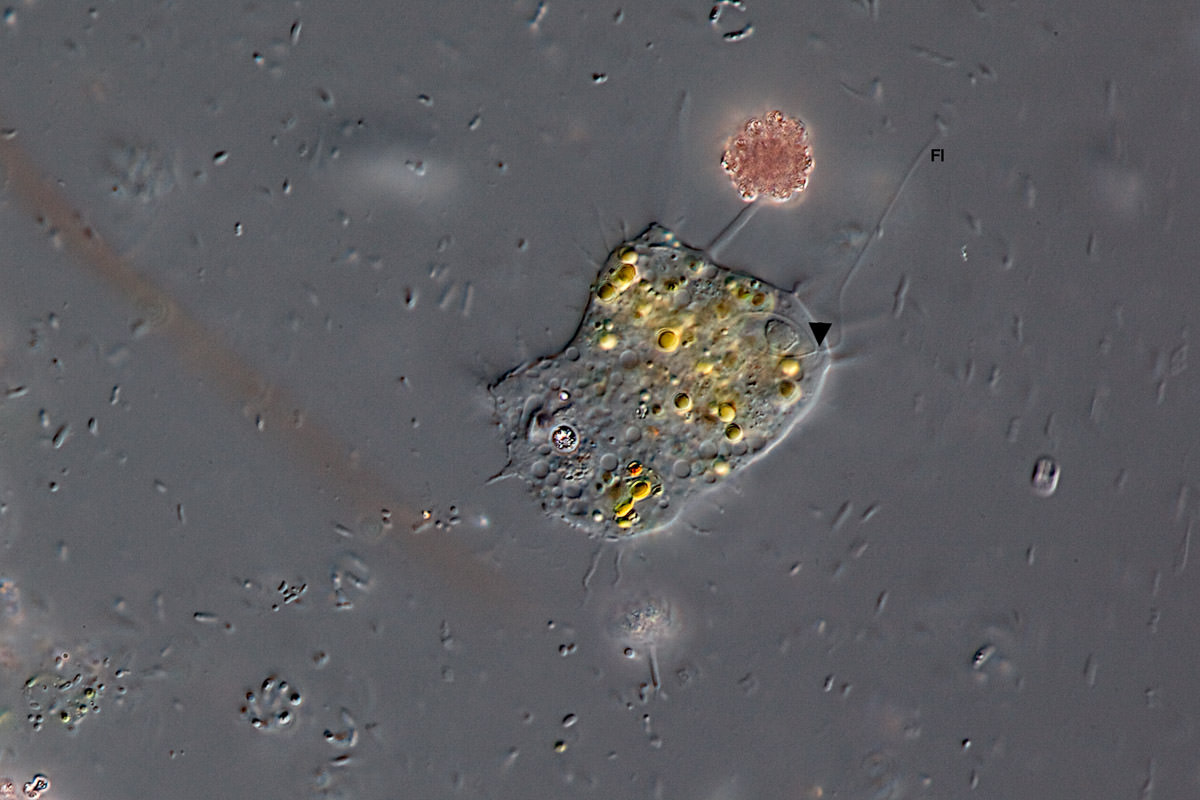
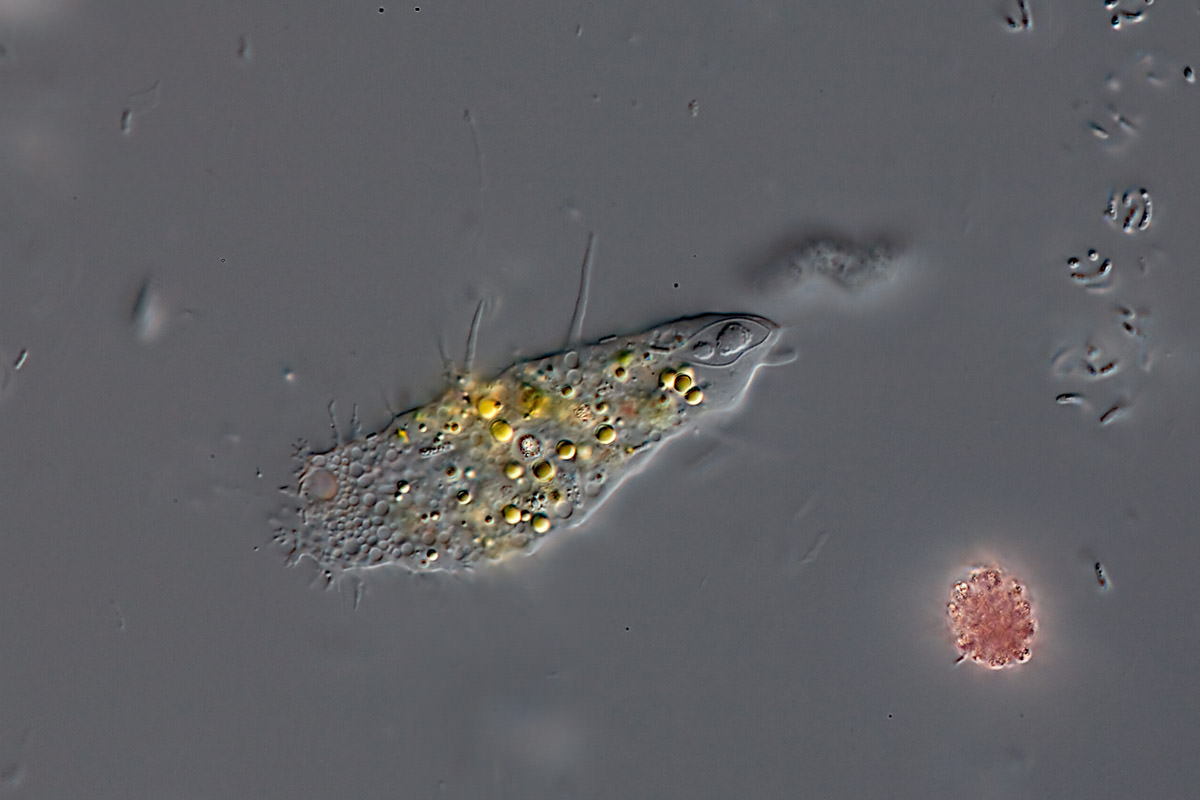
Mastigamoeba aspera Schulze 1875
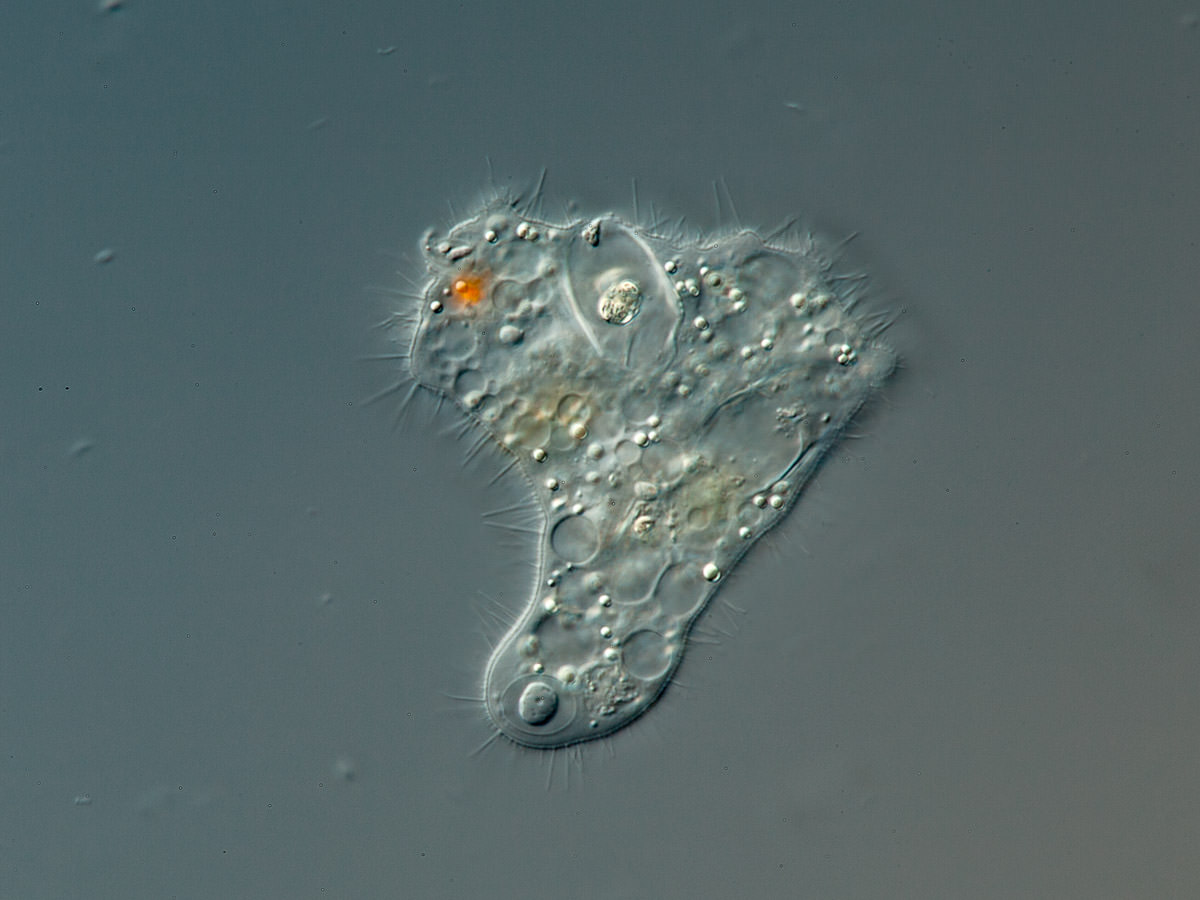
Mastigamoeba setosa Goldschmidt 1907
With scales and chitinous bristles. Sexual reproduction by anisogamy.
With scales and chitinous bristles. Sexual reproduction by anisogamy.
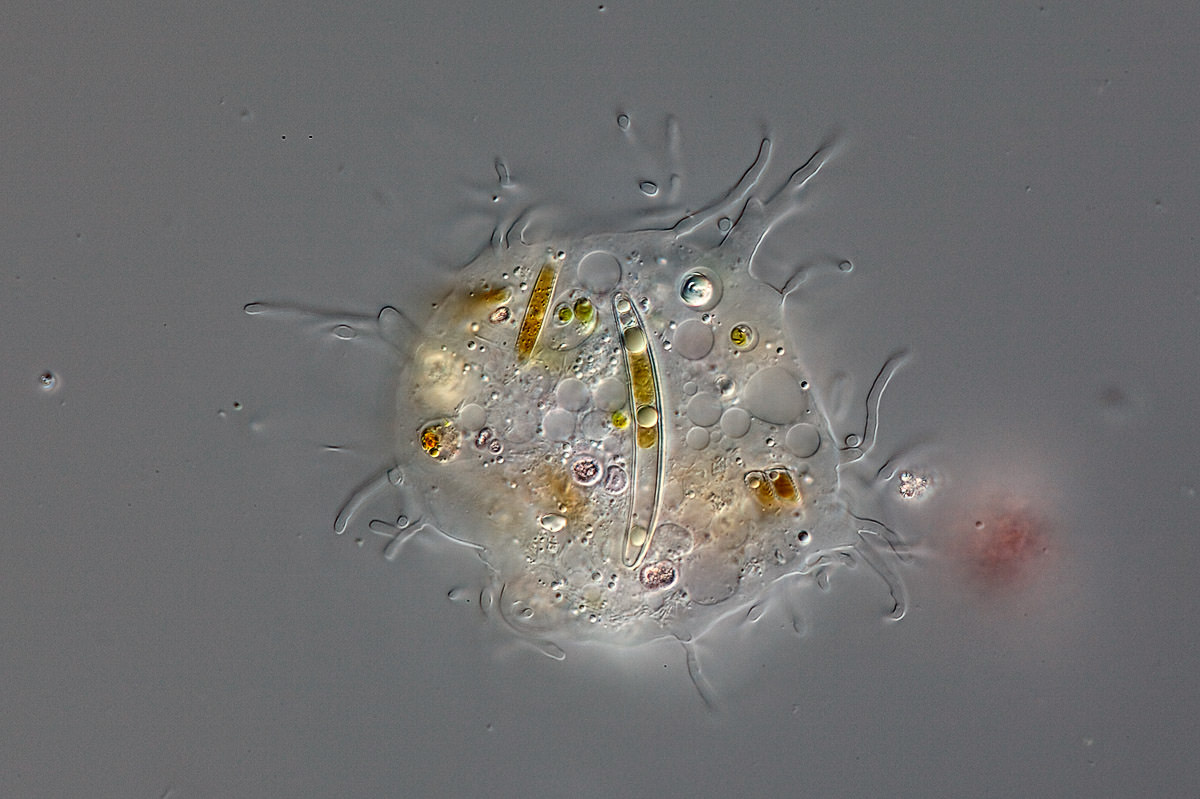
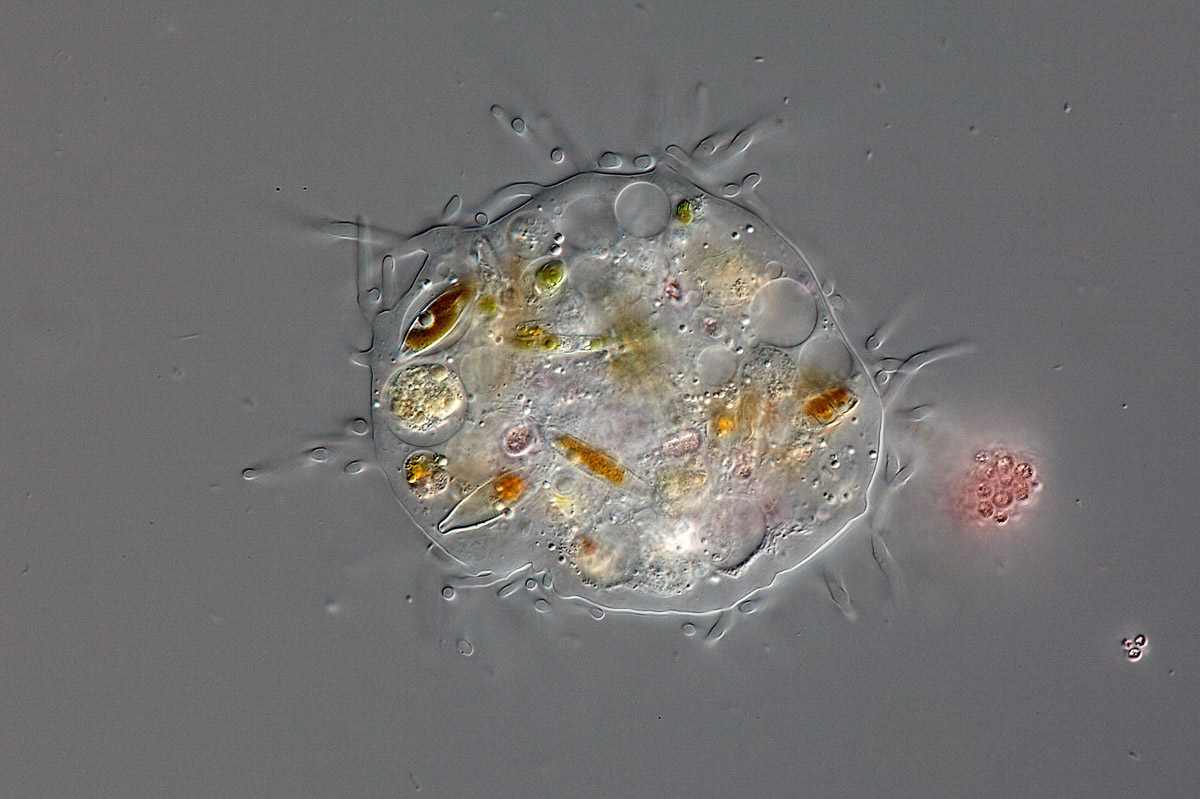
Mastigamoeba sp.
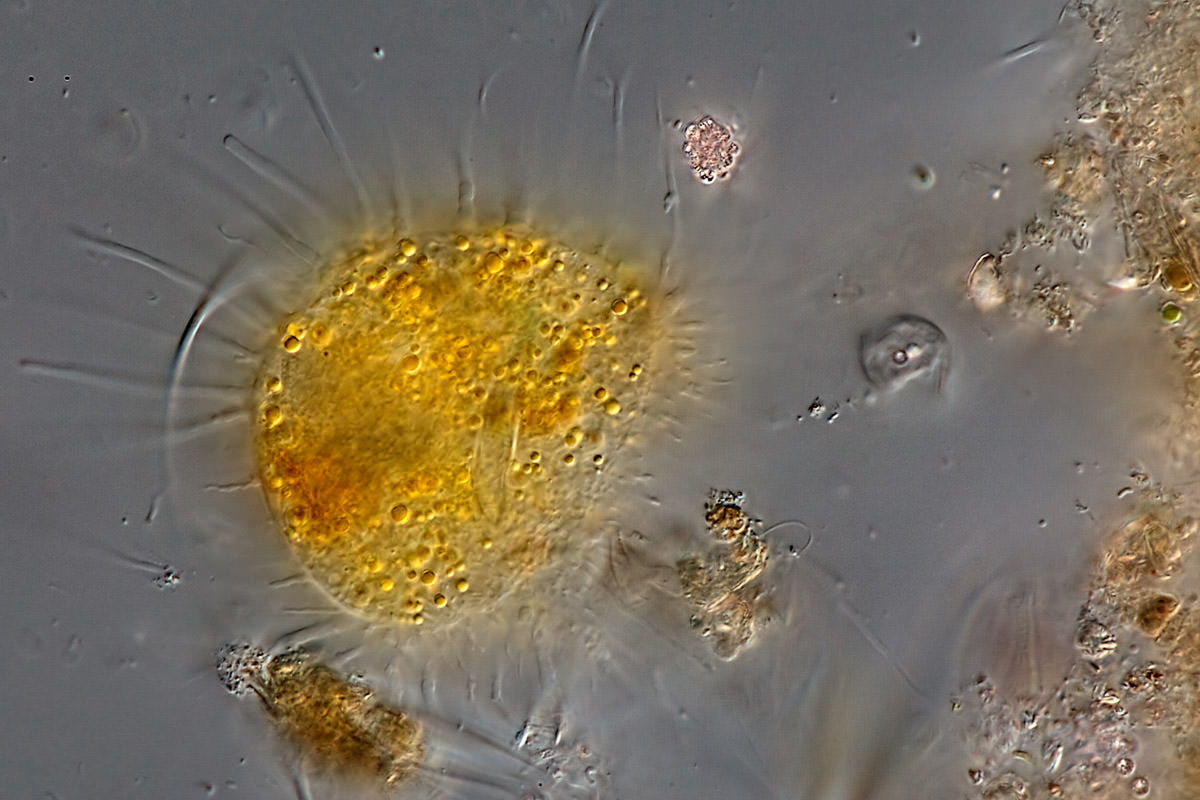
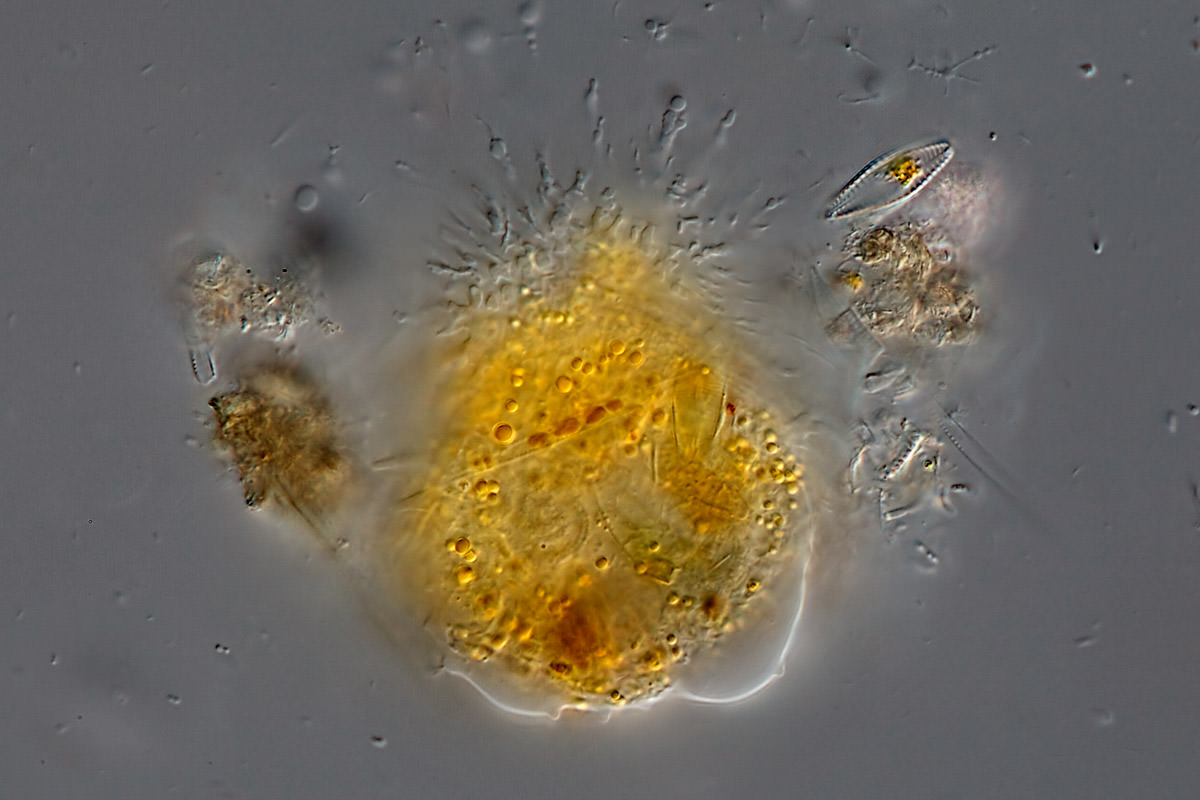
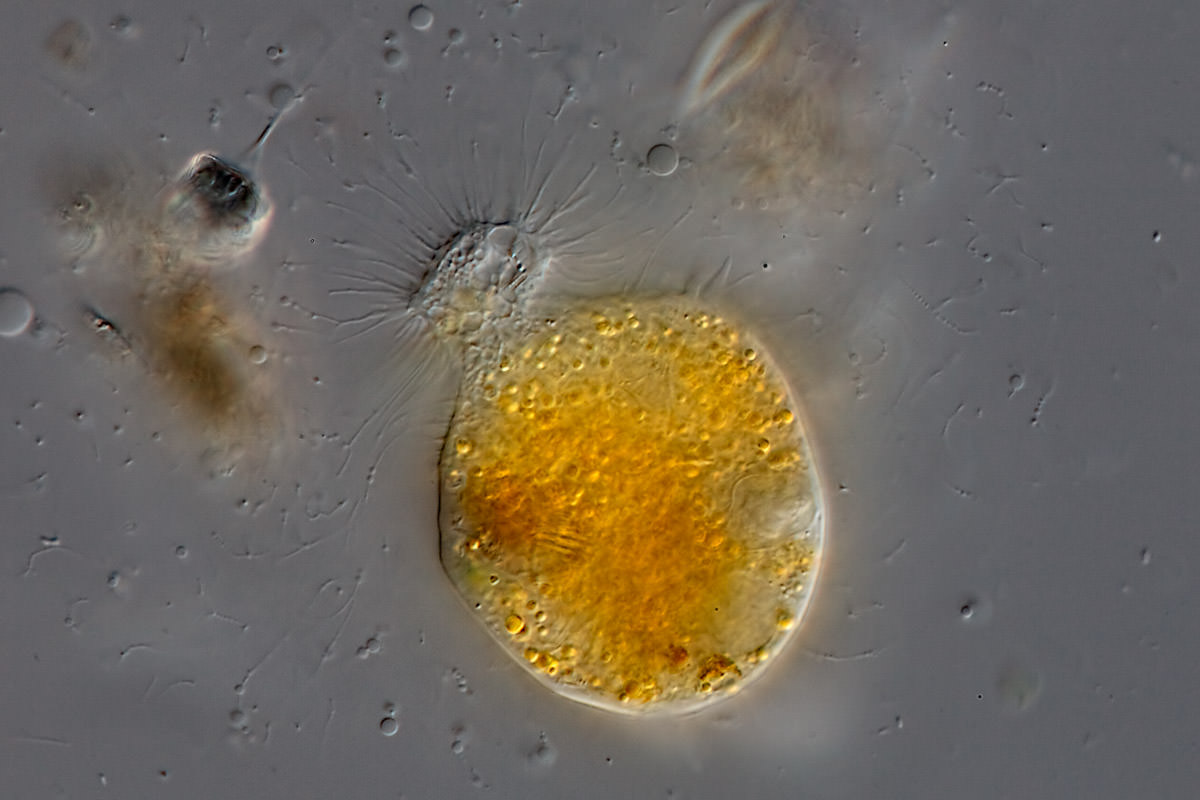
Mastigamoeba sp.
2. Pelomyxaidae Schulze 1877
Anaerobic or micro aerobic flagellated amoebae with slow-beating monokinetid or immobile polykinetids.
2.1. Pelomyxa Greeff 1874
Large amoebae (up to 3 mm) with large anterior pseudopod and posterior uroid. Short cilia at some stages of the life cycle. Polymorphic life cycle with multinucleate stages; with symbionts.
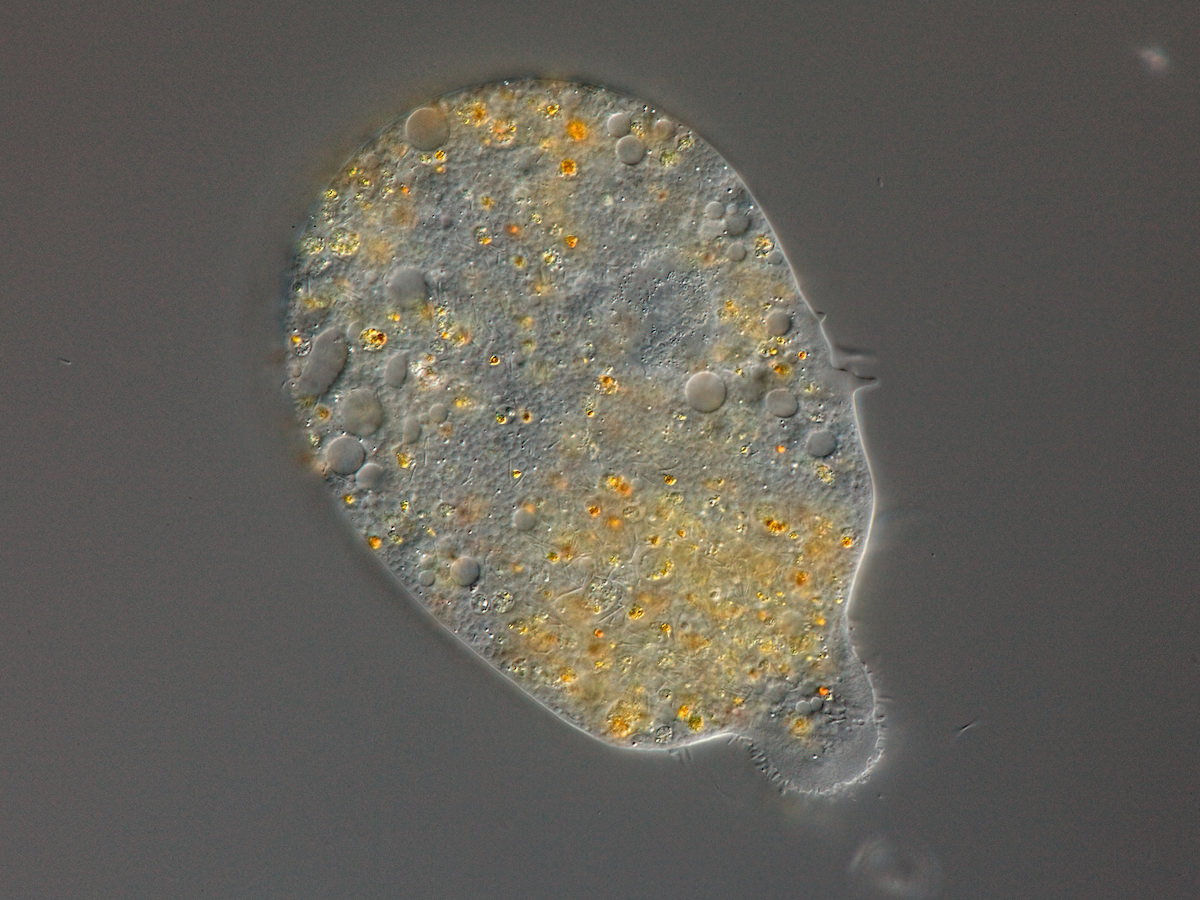
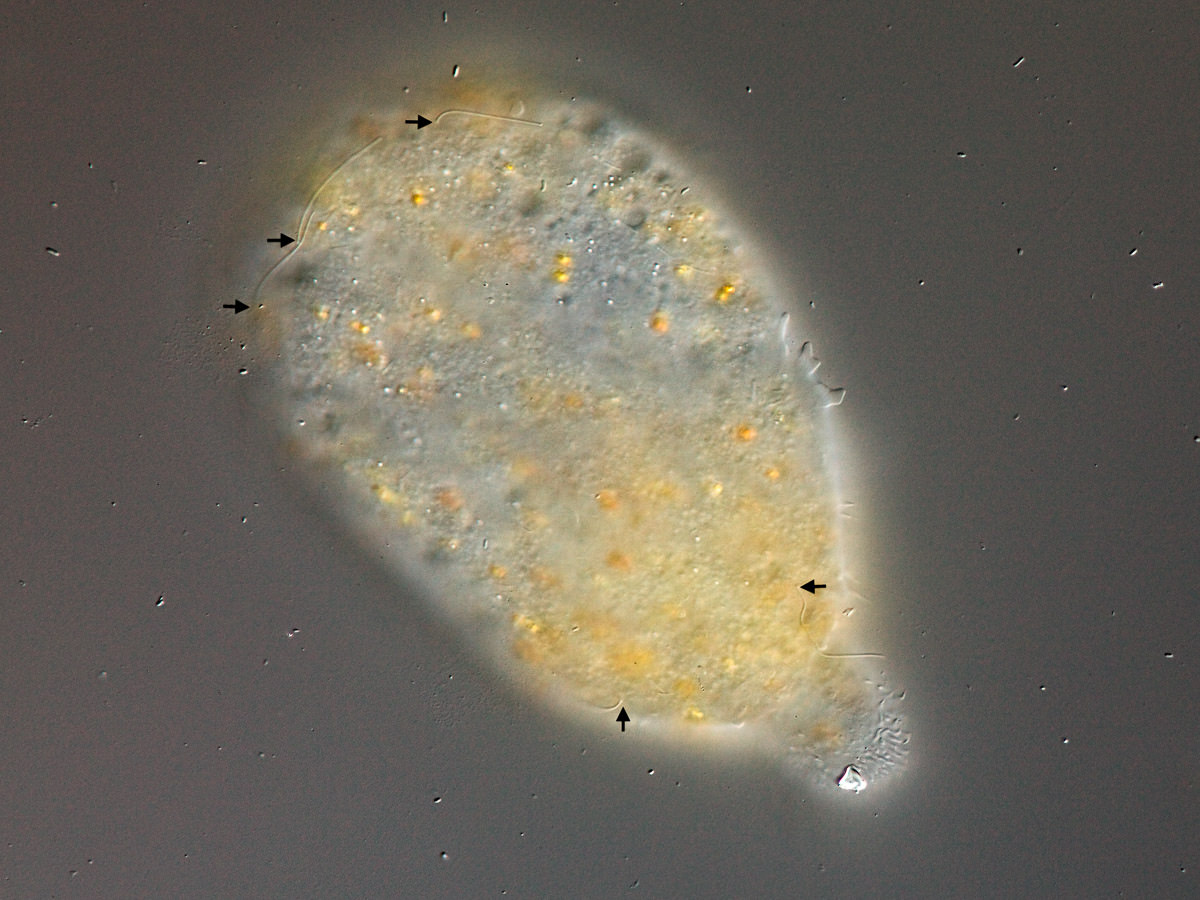
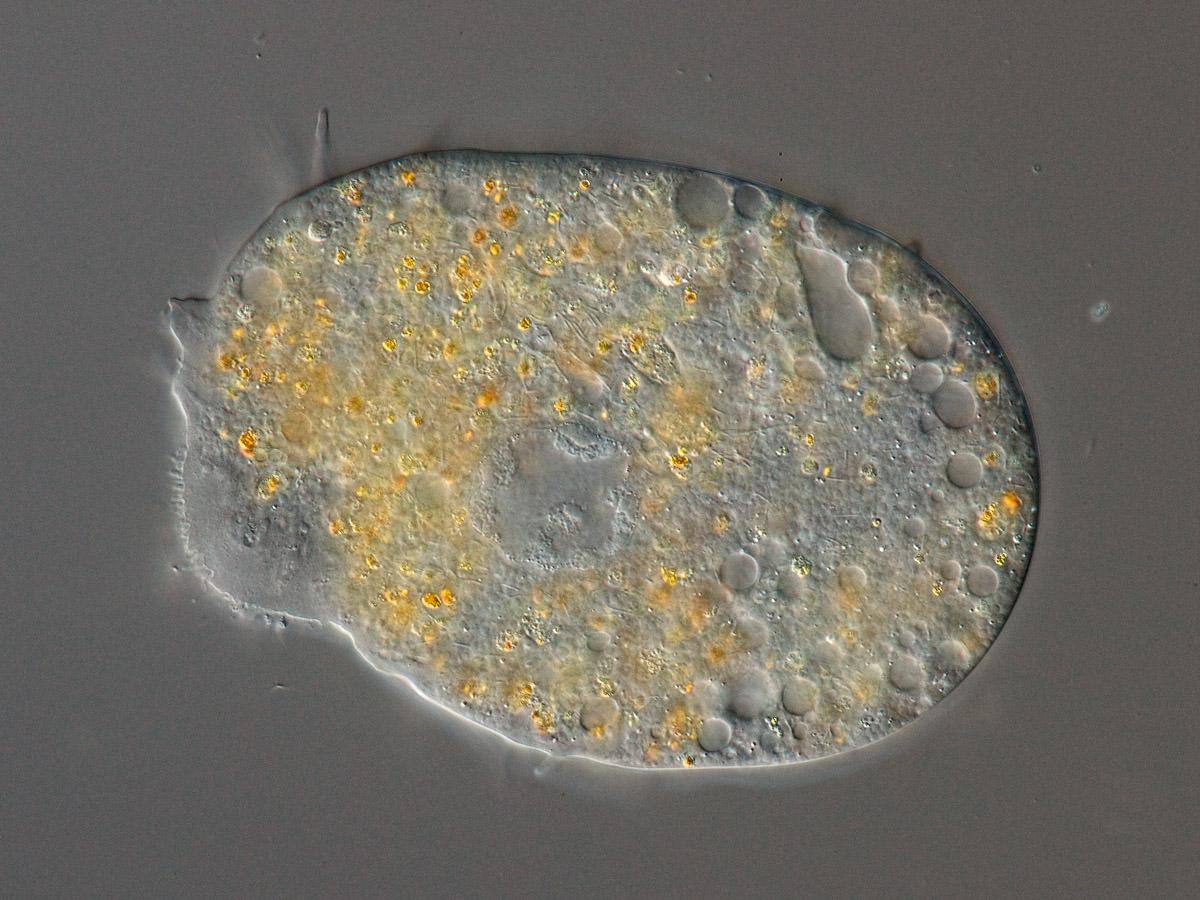
Pelomyxa palustris Greeff 1874
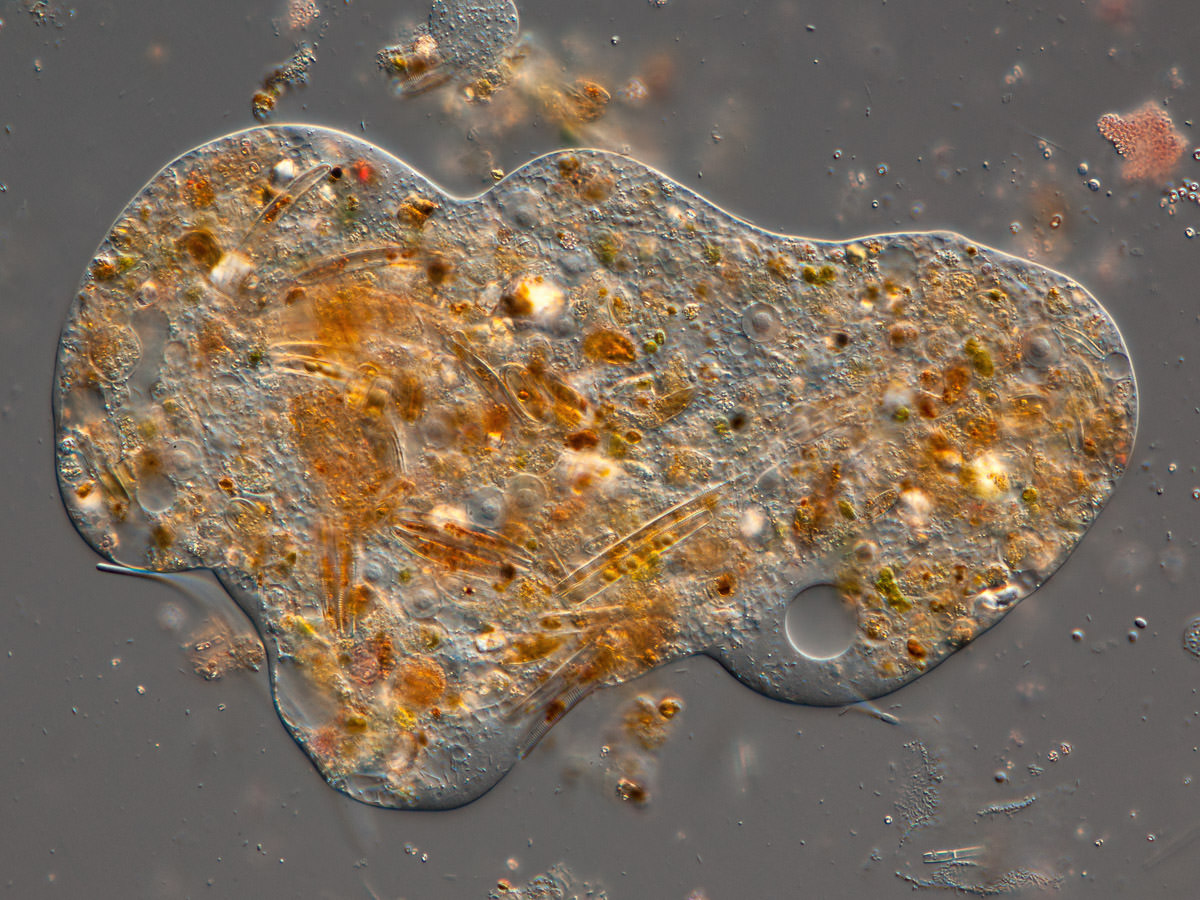
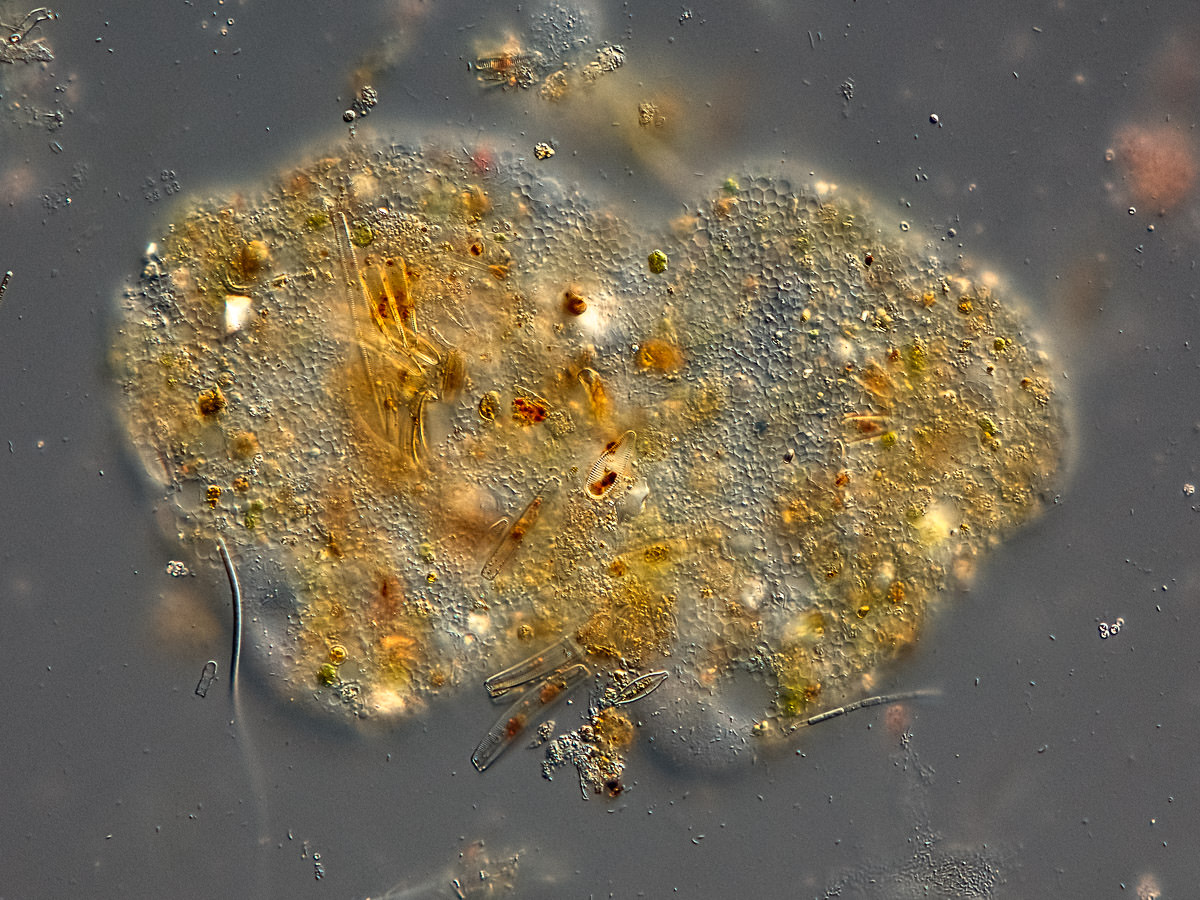
Pelomyxa gruberi Frolov, Goodkov, Chystjakova, and Skarlata 2006