Chrysophyceae Pascher 1914
Predominantely ciliated cells, swimming cells biciliated – one anteriorly directed and one laterally directed; cell coverings, when present, include organic scales, silica scales, organic lorica, and cellulose cell wall; eyespots present or absent; statospores.
Predominantely ciliated cells, swimming cells biciliated – one anteriorly directed and one laterally directed; cell coverings, when present, include organic scales, silica scales, organic lorica, and cellulose cell wall; eyespots present or absent; statospores.
1. Chromulinales Pascher 1910
Swimming cells with only one cilium visible by light microscopy.
1.1. Chromulinaceae Engler 1897
1.1.1. Cyclonexis Strokes 1886
Colonies free-swimming, consisting of 4-34 cells compactly arranged to form a circular plate with an open space in the center. Cohesion rather loose and colonies easily break up. Cells naked, with two unequal cilia, two contractile vacuoles, one or two chloroplasts and one species with eyespots. No sexual reproduction observed.
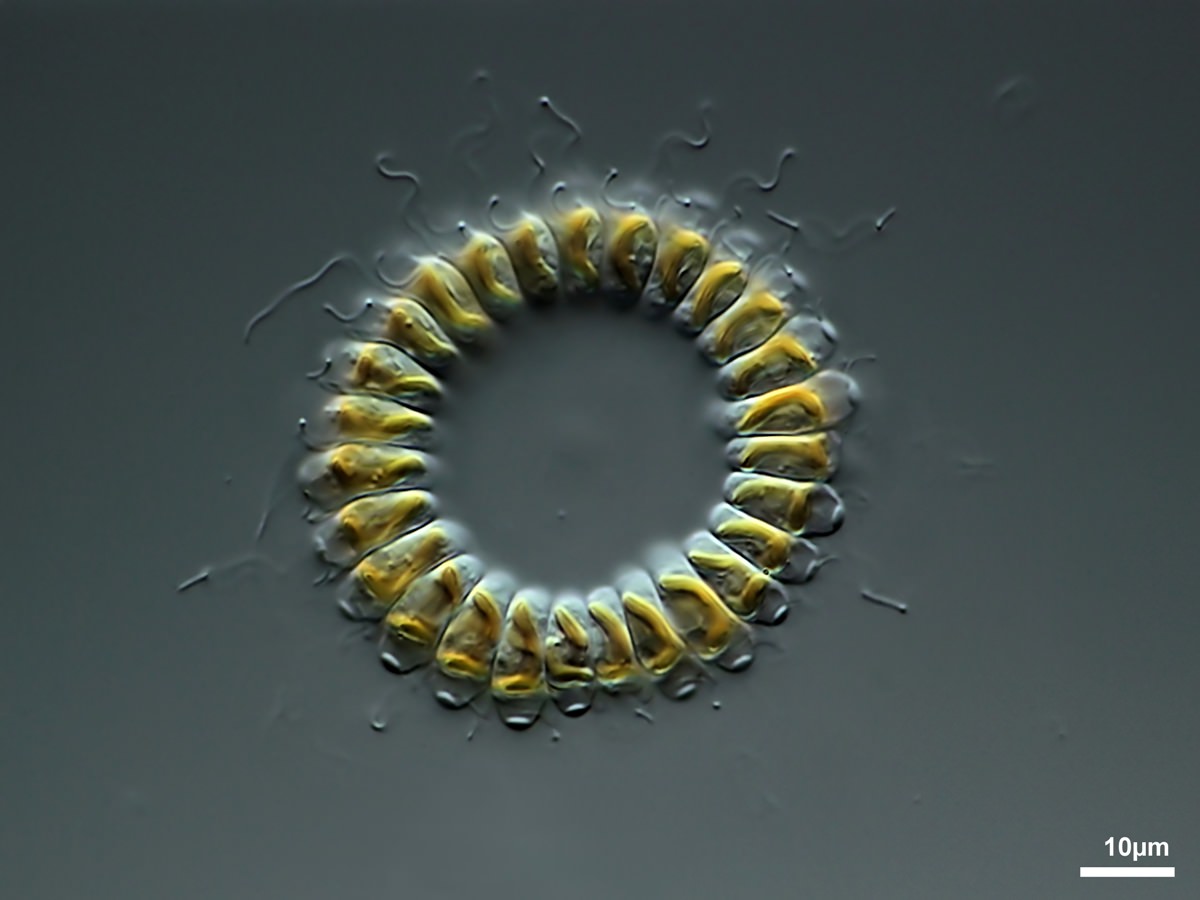

Cyclonexis sp.
1.2. Dinobryaceae Ehrenberg 1834
1.2.1. Dinobryon Ehrenberg 1834
Cells free-living, surrounded by a lorica, solitary or united in branched colonies. Lorica cylindrical, vase- or funnel-shaped, with smooth or undulated walls, in a few species with spiral thickenings.
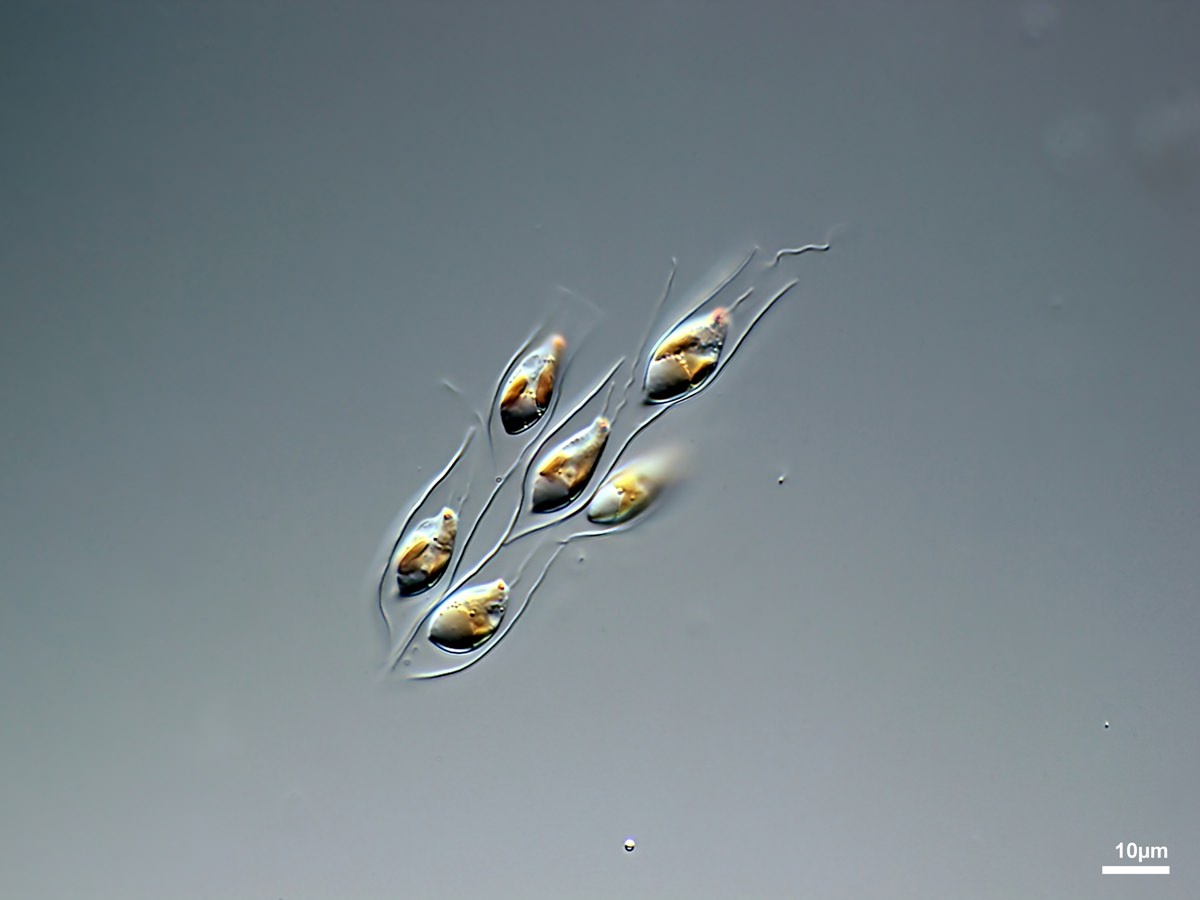
Dinobryon sp.
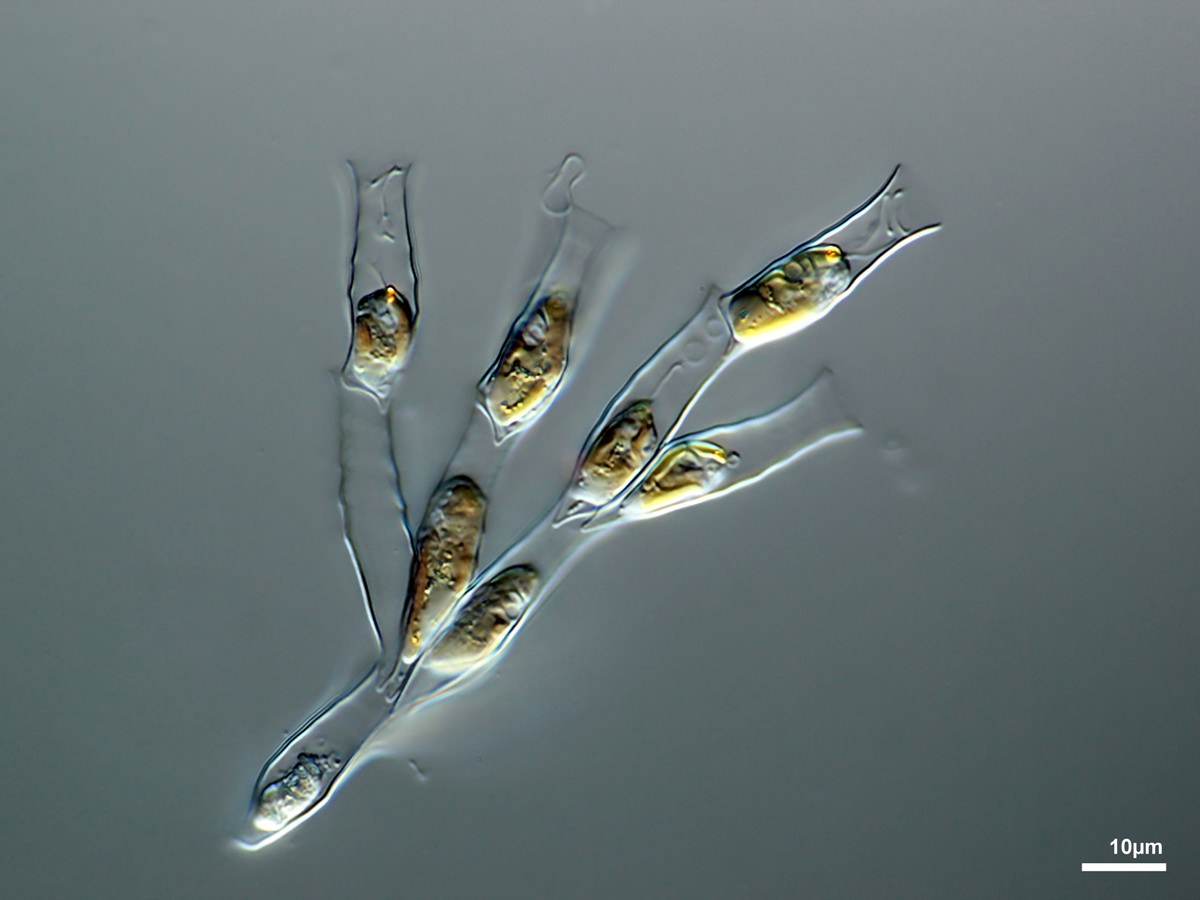

Dinobryon pediforme (Lemmermann) Steinecke 1916
1.2.2. Epipyxis Ehrenberg 1838
Lorica solitary, clustered or forming colonies. Lorica constructed of overlapping scales.
Lorica solitary, clustered or forming colonies. Lorica constructed of overlapping scales.
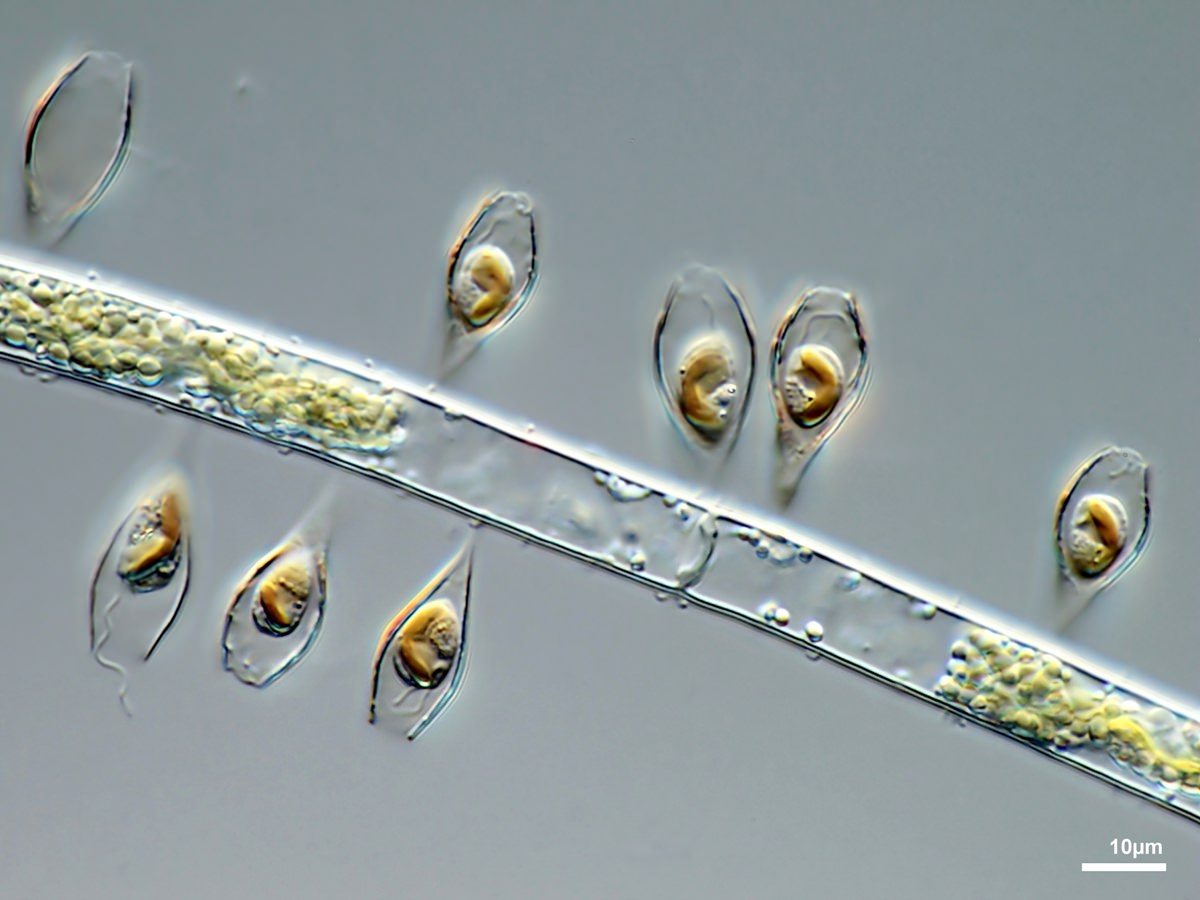
Epipyxis utriculus Ehrenberg 1838
1.3. Paraphysomonadida Scoble and Cavalier-Smith 2014
Colorless, bicilaited, heterotrophic; with silicious spine or basket scales.
1.3.1. Paraphysomonas De Saedeleer 1930, emend. Scoble and Cavalier-Smith 2014
Cells colorless, solitary, spherical to slightly ovate or elongate in shape, covered with siliceous spine scales and at the anterior end bearing two cilia of unequal length.
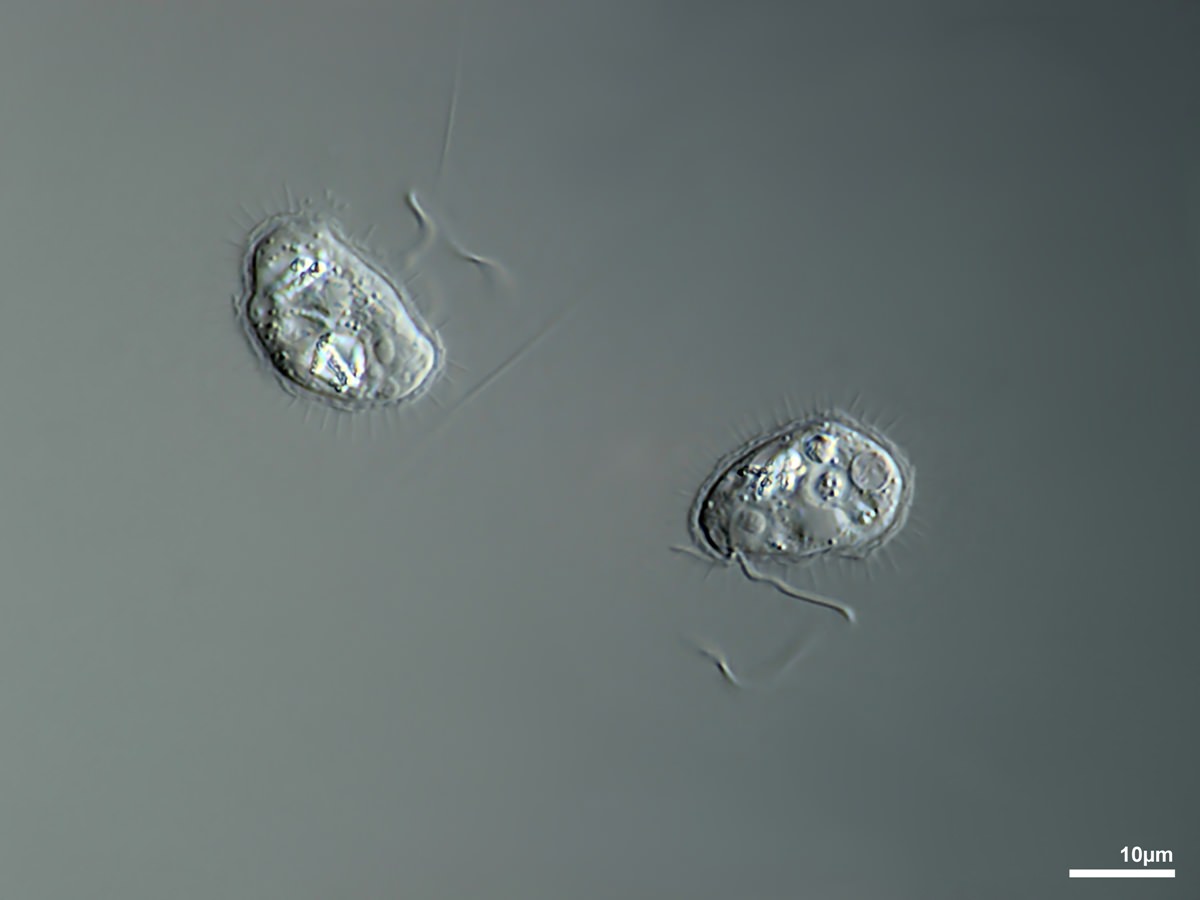
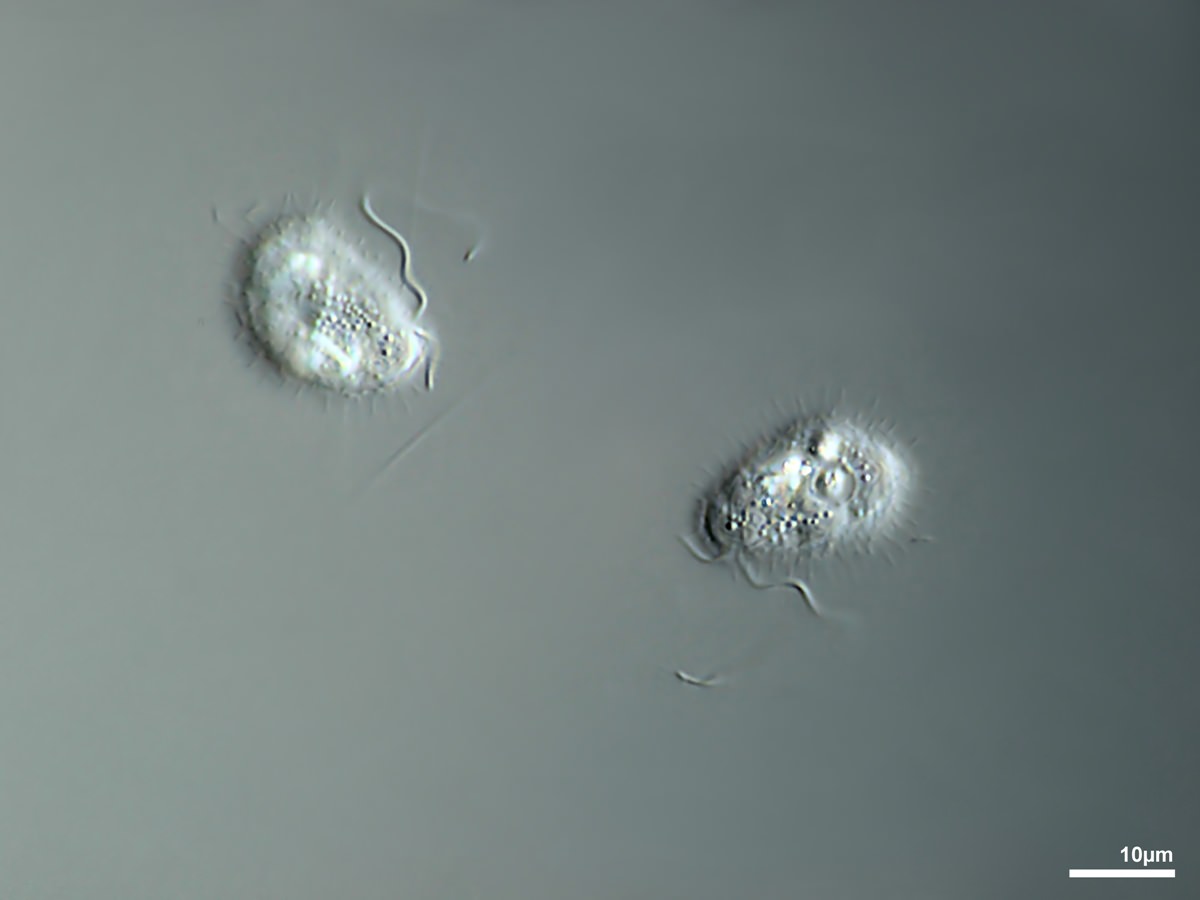
Paraphysomonas sp.
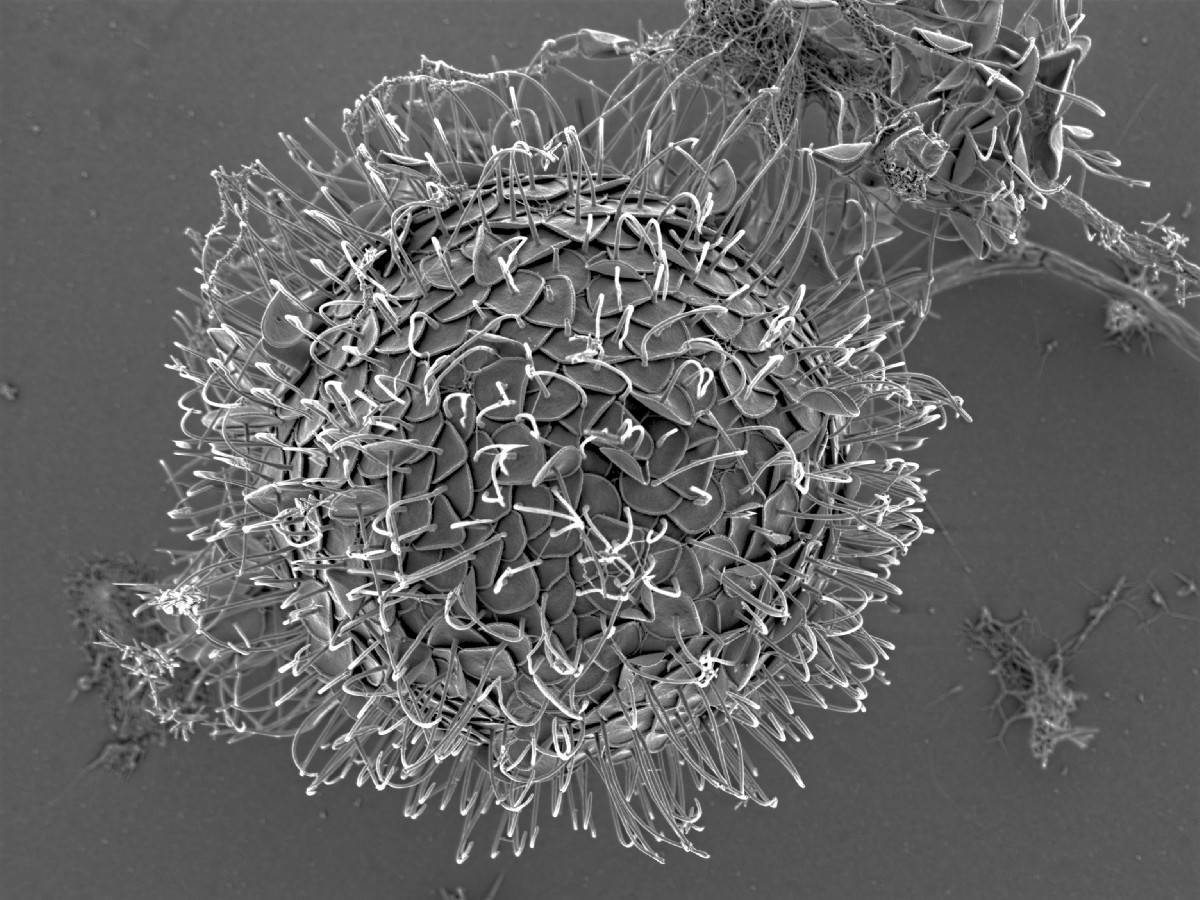
Paraphysomonas sp.
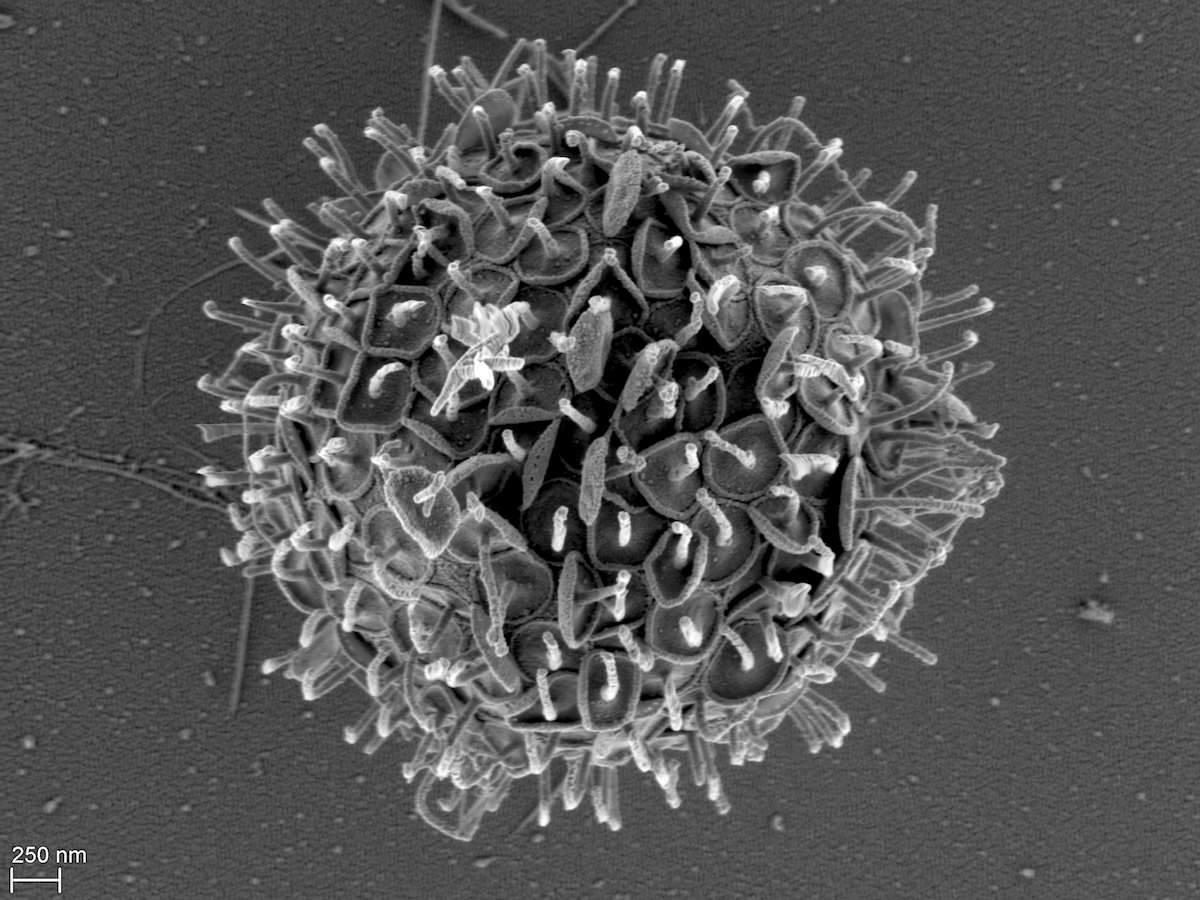
Paraphysomonas sp.
1.3.2. Clathromonas Scoble and Cavalier-Smith 2014
Cells colorless, solitary, spherical to slightly ovate or elongate in shape, covered with siliceous basket scales and at the anterior end bearing two cilia of unequal length.
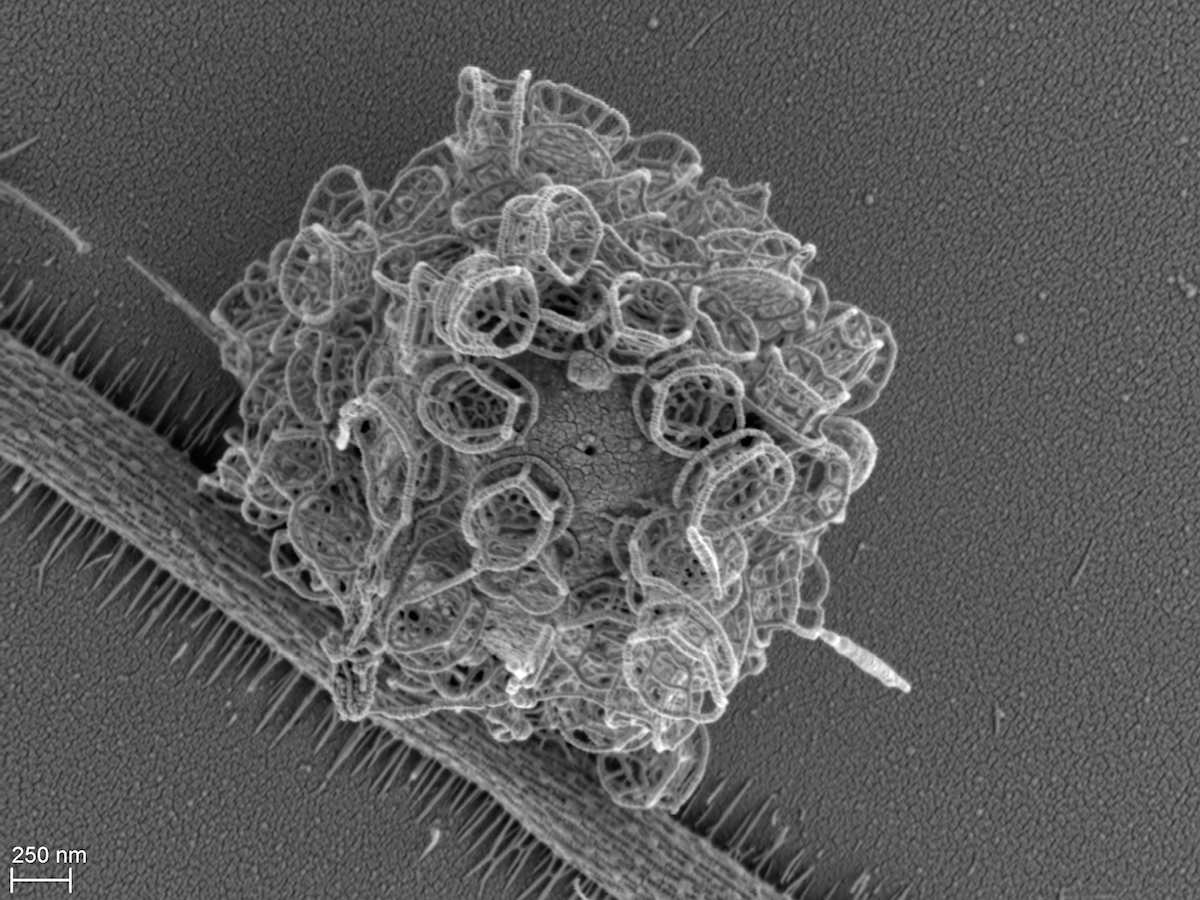
Clathromonas sp. Scoble and Cavalier-Smith 2014
1.4. Chrysamoebaceae Poche 1913
1.4.1. Chrysamoeba Klebs 1892
Cells naked, forming simple or branched pseudopodia. Often loose colonies. With or without cilia, with or without eyespots.
Cells naked, forming simple or branched pseudopodia. Often loose colonies. With or without cilia, with or without eyespots.
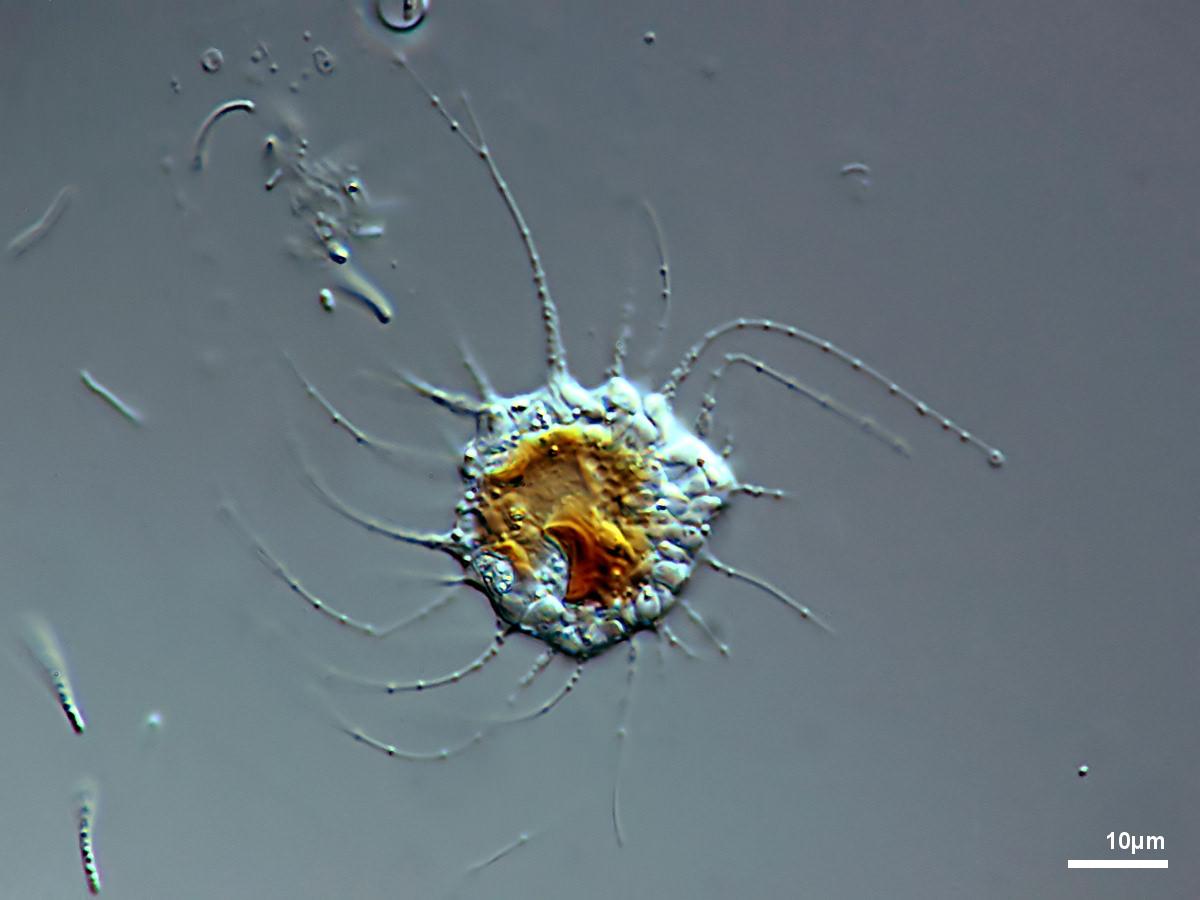
Chrysamoeba radians Klebs 1892
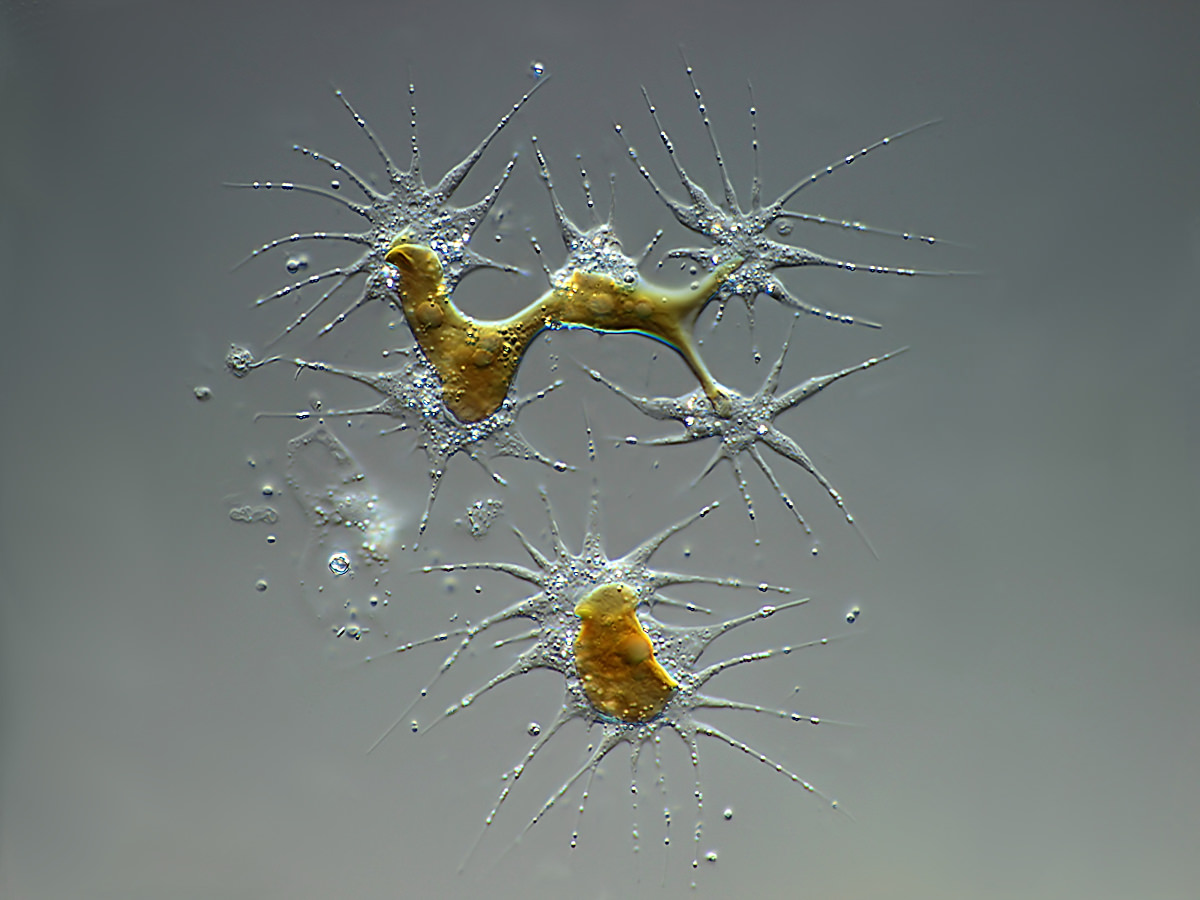
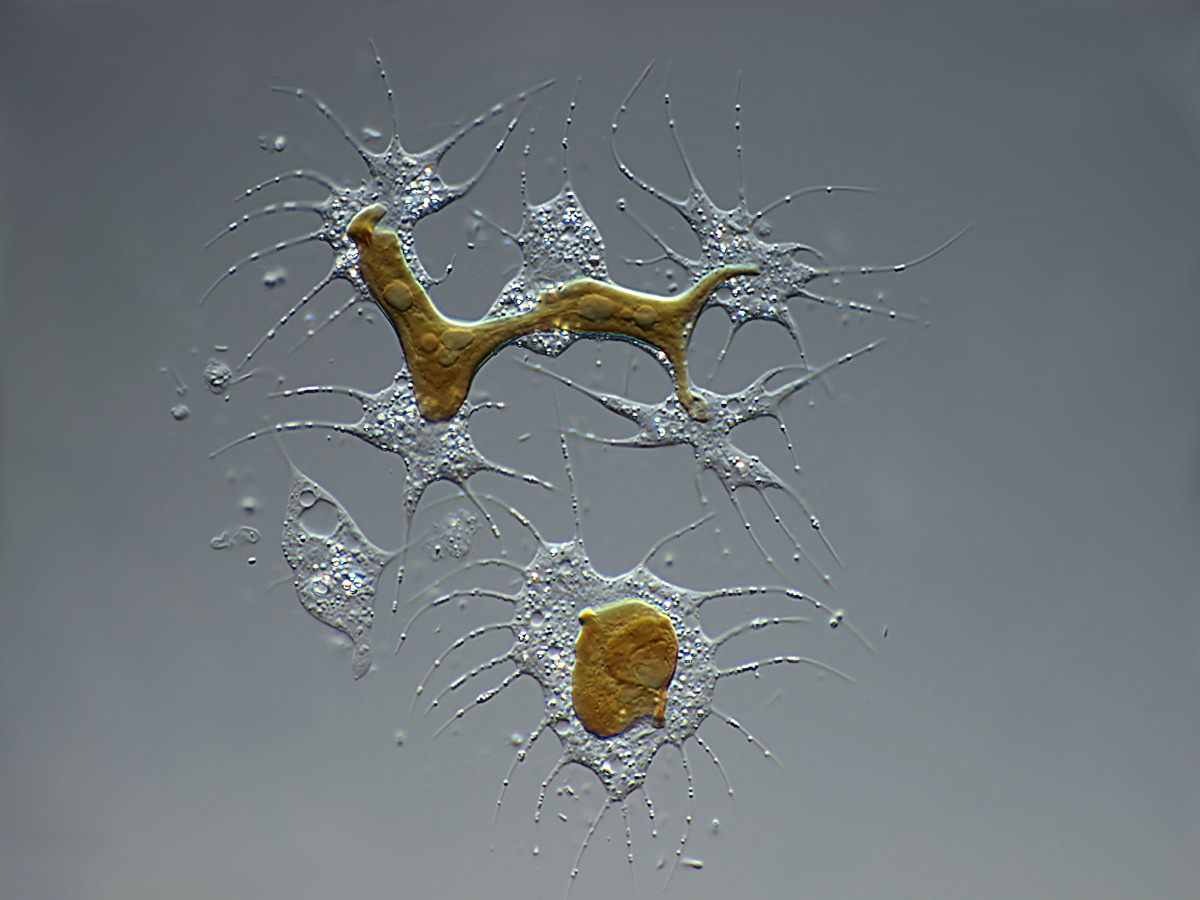
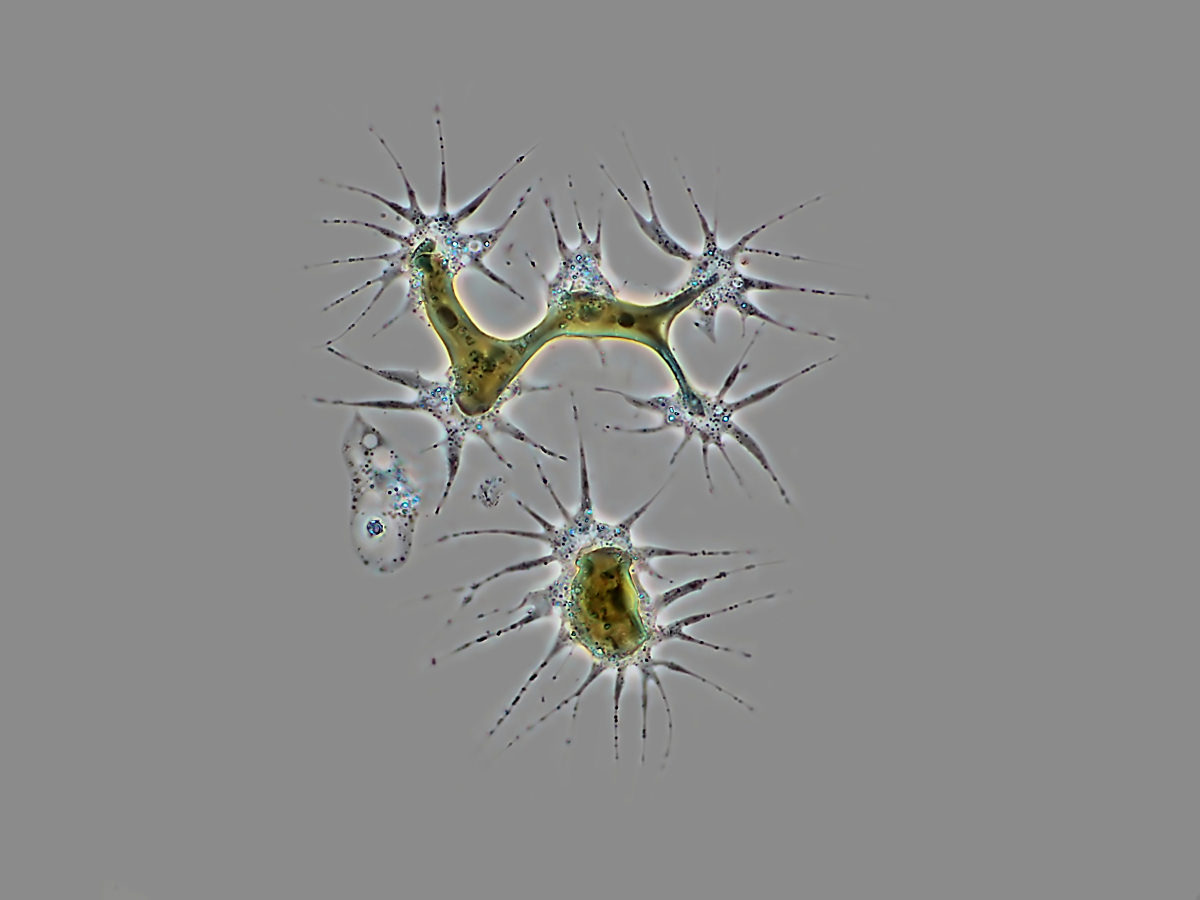
Chrysamoeba sp.
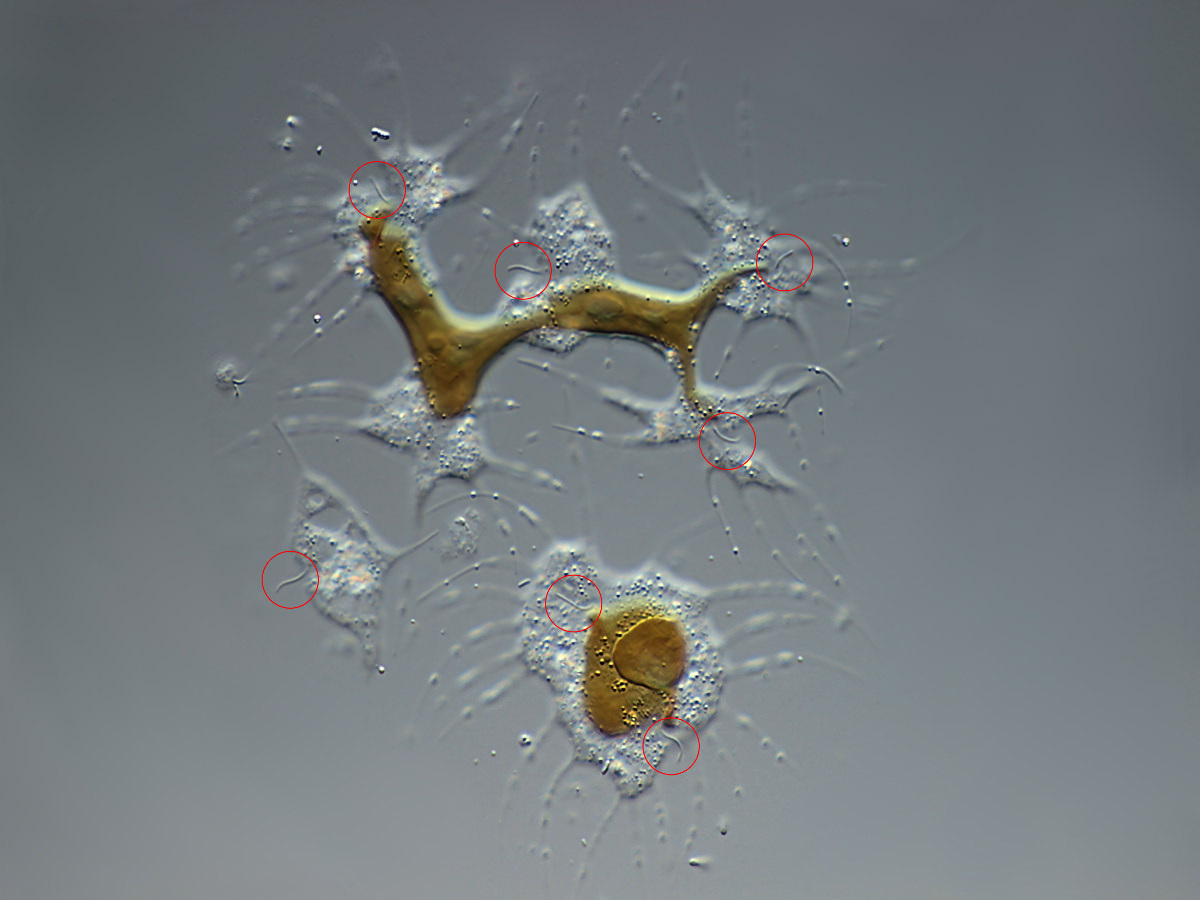
This appears to be a colony of 5 ciliated cells (red circles) that share a chromatophore. Maybe this is a devision.
This appears to be a colony of 5 ciliated cells (red circles) that share a chromatophore. Maybe this is a devision.
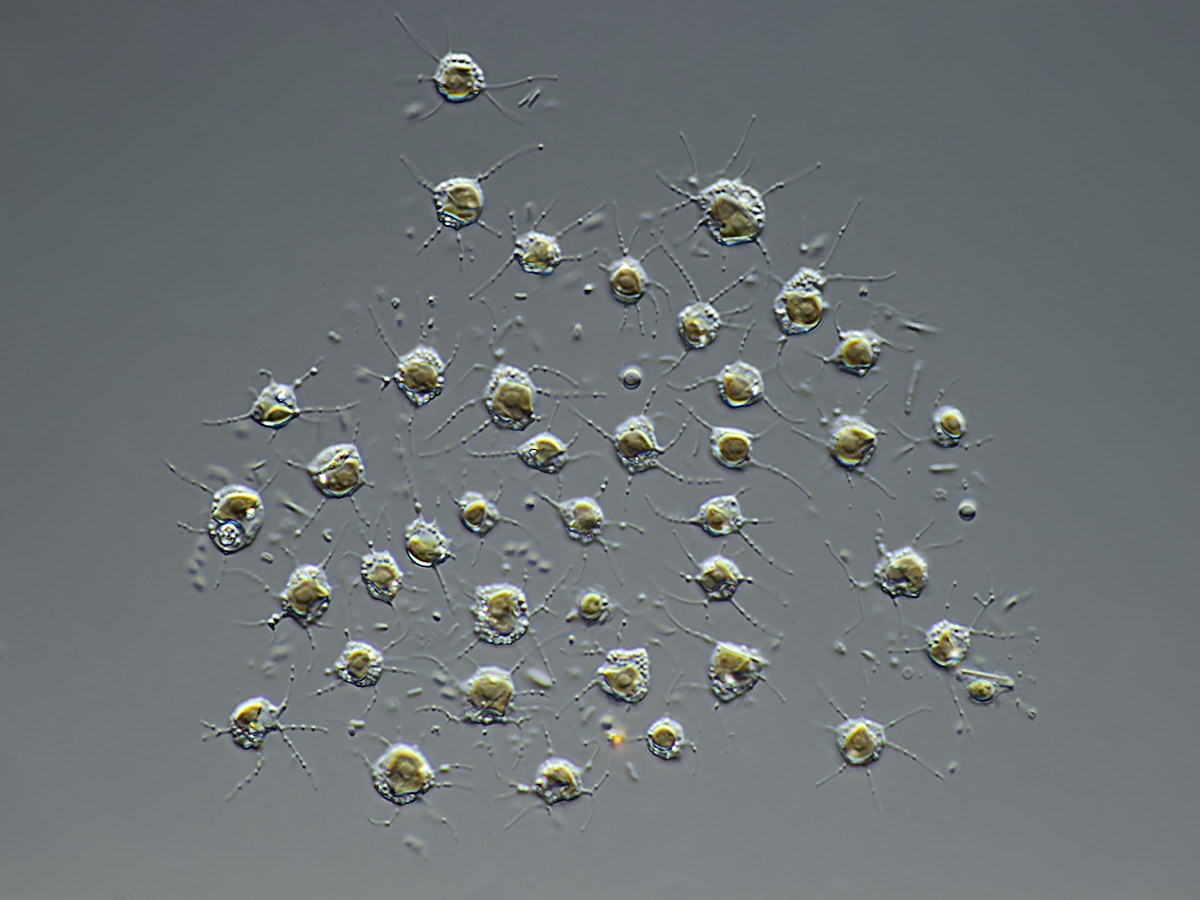
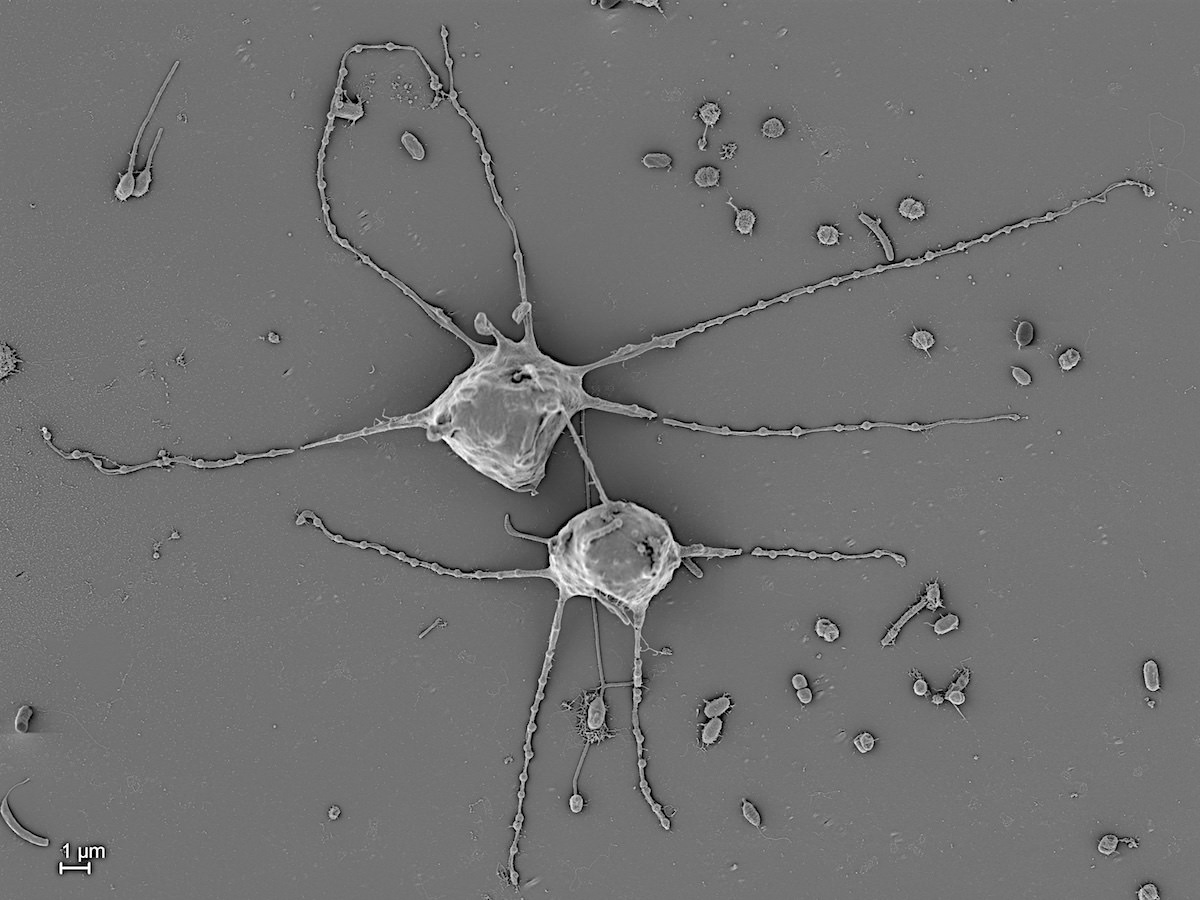
Chrysamoeba sp.
1.4.2. Chrysostephanosphaera Scherffel 1911
Colonies discoid, consisting of 42-32 naked cells with one to four chloroplasts and two contractile vacuoles. Numerous fine rhizopodia extend from the colony, which is surrounded by numerous globular, inorganic bodies produced endogenously.
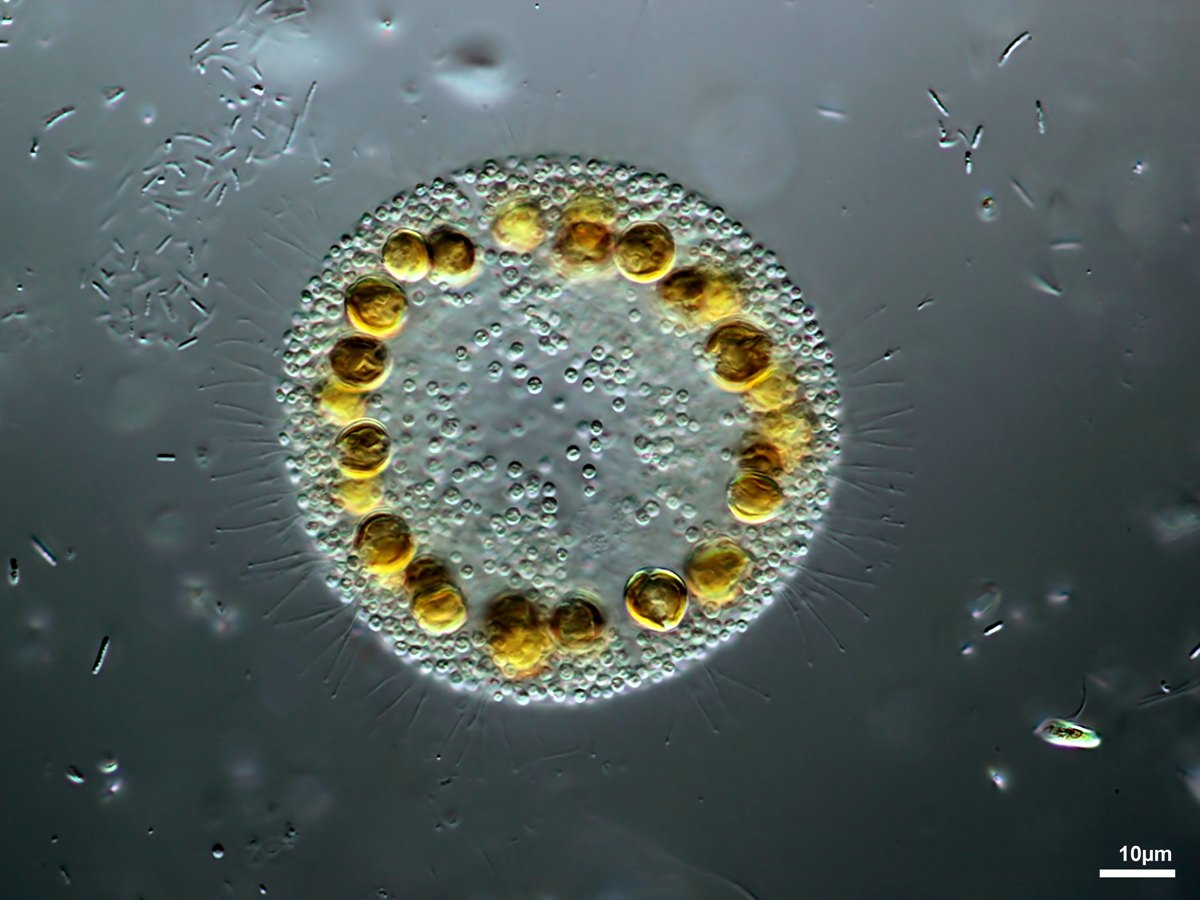

Chrysostephanosphaera globulifera Scherffel 1911
2. Hibberdiales Andersen 1989
2.1. Stylococcaceae Lemmermann 1899
2.1.1. Lagynion Pascher 1912
Cells amoeboid, solitary, surrounded by a lorica. Lorica flask-shaped with or without long neck, in most species fixed to a substratum by one side and often brownish with iron salts. Cells spherical, not fixed within the lorica. Apically they have delicate, branched pseudiopida emerging through the lorica neck. 1-2 chloroplasts, eyespots absent, reproduction by division.
Cells amoeboid, solitary, surrounded by a lorica. Lorica flask-shaped with or without long neck, in most species fixed to a substratum by one side and often brownish with iron salts. Cells spherical, not fixed within the lorica. Apically they have delicate, branched pseudiopida emerging through the lorica neck. 1-2 chloroplasts, eyespots absent, reproduction by division.
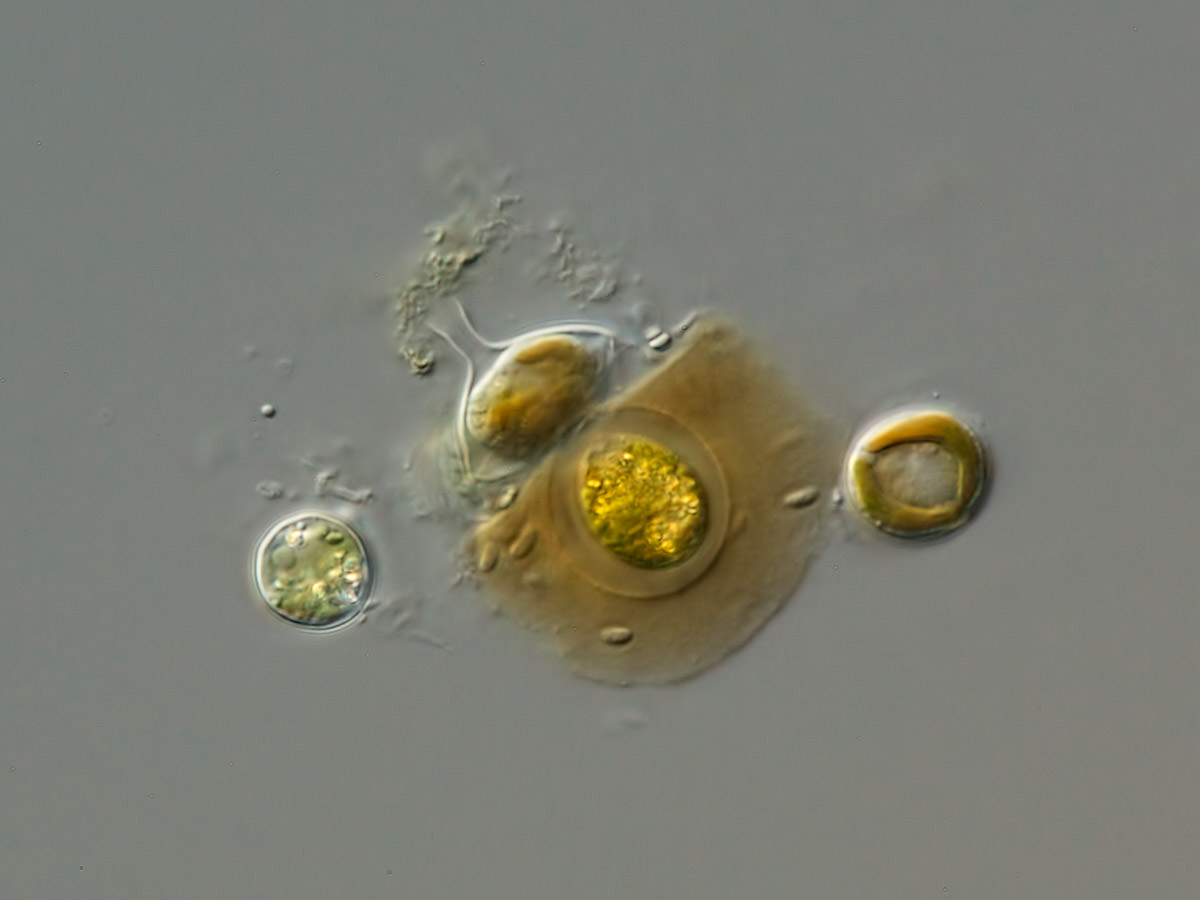
Lagynion sp.
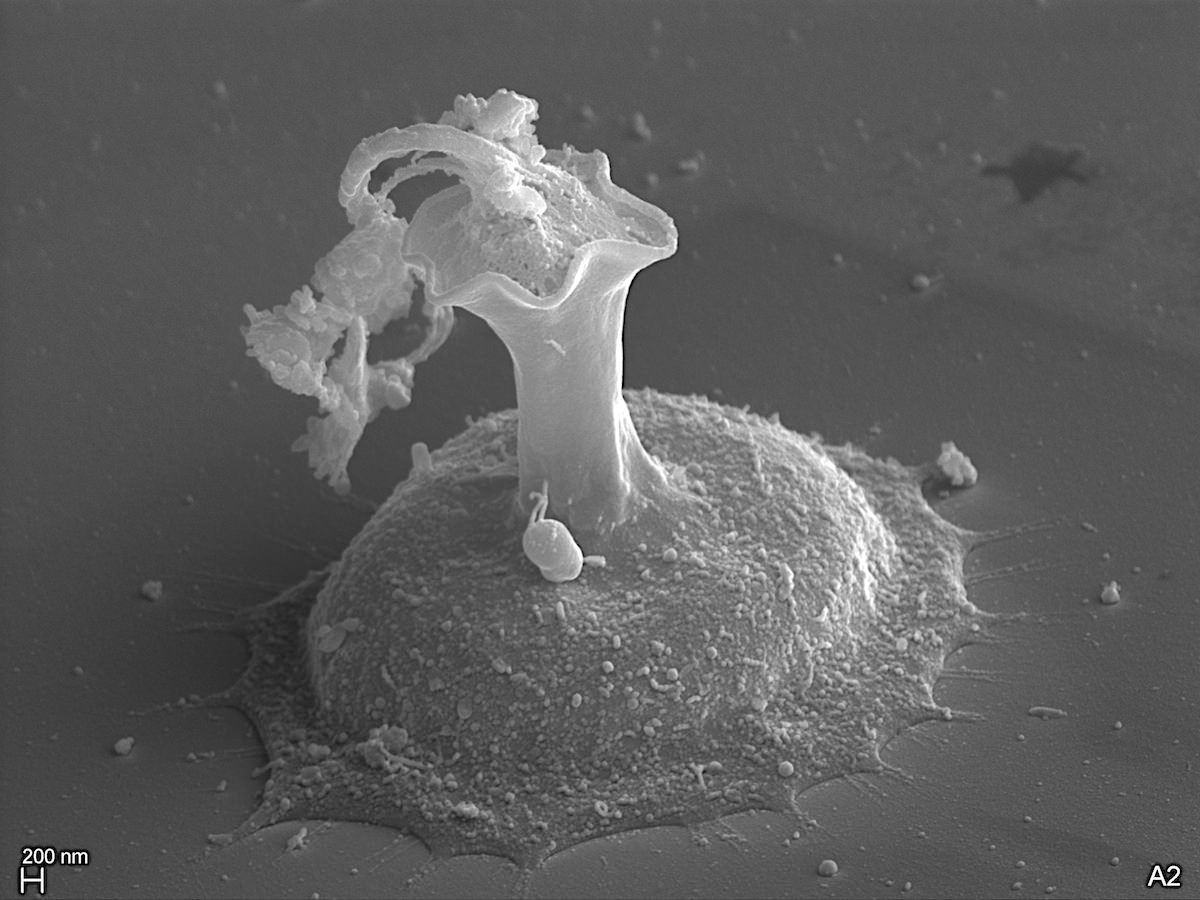
Lagynion sp.